Chemistry
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryA new microbead proves effective as a plastic-free skin scrubber
The nonplastic polymer cleaned up eyeliner and permanent marker and broke down into molecules related to sugar and amino acids.
By Skyler Ware -
 Life
LifeSheep earwax can record a dangerous diet
Sheep that eat death camas plants record the toxic meal in their earwax, a goopy health data repository that researchers are increasingly exploring.
By Jake Buehler -
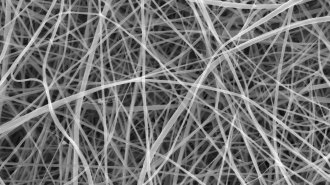 Materials Science
Materials ScienceStarchy nanofibers shatter the record for world’s thinnest pasta
The fibers, made from white flour and formic acid, average just 372 nanometers in diameter and might find use in biodegradable bandages.
By Skyler Ware -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists identify a long-sought by-product of some drinking water treatments
Chlorine-based water treatments create many by-products, but one has been elusive. Its identification sets the stage for studying its health effects.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsA single enzyme can alter the vibrant colors in parrot plumage
Tweaking the chemical composition of a parrot-specific pigment can shift feathers from red to yellow or green.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryWork on protein structure and design wins the 2024 chemistry Nobel
David Baker figured out how to build entirely new proteins. Demis Hassabis and John Jumper developed an AI tool to predict protein structures.
By Meghan Rosen and Andrea Tamayo -
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists may have an explanation for why some batteries don’t last
A long-standing idea of why lithium ion batteries die focuses on lithium movement into the cathode. Instead, hydrogen may be to blame.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentA biogeochemist is tracking the movements of toxic mercury pollution
Exposing the hidden movements of mercury through the environment can help reduce human exposure.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA materials scientist seeks to extract lithium from untapped sources
Lithium is an essential ingredient for batteries in electric vehicles but getting enough will become a problem.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Climate
ClimateZapping sand to create rock could help curb coastal erosion
Low voltages generated minerals that help bind the sand into erosion-resistant rock, offering hope for shorelines ravaged by waves.
By Sid Perkins -
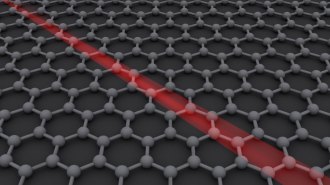 Physics
PhysicsThe world’s fastest microscope makes its debut
Using a laser and an electron beam, the microscope can snap images of moving electrons every 625 quintillionths of a second.
By Skyler Ware -
 Chemistry
ChemistryOld books can have unsafe levels of chromium, but readers’ risk is low
An analysis of a university collection found that the vibrant pigments coating some Victorian-era tomes exceed exposure limits for the heavy metal.
By Skyler Ware