Astronomy
-
 Physics
PhysicsWhen entering a black hole, fasten your seat belt
Rapidly spinning black holes can generate turbulence, a new analysis shows.
By Andrew Grant -
 Astronomy
AstronomyGiant rings encircle young exoplanet
Stretching 90 million kilometers from their center, 37 stripes of dust around exoplanet were probably crafted by moons.
-
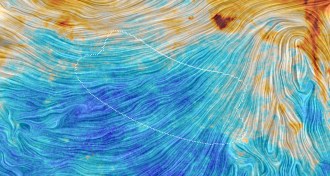 Cosmology
CosmologyDust erases evidence for gravity wave detection
The claimed detection of primordial gravitational waves does not hold up after taking into account galactic dust, a new analysis concludes.
By Andrew Grant -
 Astronomy
AstronomyNeptune-like worlds could become habitable
Mini-Neptunes can drift toward their stars and lose their atmospheres, leaving behind ice-rich rocky cores that can become watery worlds.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyOldest solar system unearthed by Kepler
Five rocky planets orbit the 11.2-billion-year-old star Kepler 444, suggesting that Earth-sized worlds formed in the early universe.
-
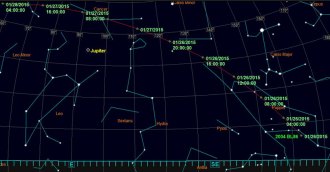 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceLarge asteroid buzzes Earth
Asteroid 2004 BL86 swings by Earth today at three times the distance to the moon, the closest asteroid encounter until 2027.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyRocky planets around cool stars may have Earthlike climates
Small, rocky planets that sit close to cool stars might be able to keep spinning, creating conditions hospitable to life.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyLarge rocky planets excel at ocean building
Rocky planets a few times as massive as Earth may build deeper oceans – and sustain them for longer – than smaller worlds.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHubble telescope captures panorama of Andromeda galaxy
The Hubble Space Telescope captured a panoramic mosaic of the closest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way, mapping the light from over 100 million stars.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyPair of black holes prepare to take the plunge
A pair of supermassive black holes in a distant galaxy will likely collide in the next million years.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyKepler telescope discovers another 554 possible planets
Extra year of Kepler telescope data adds 554 possible planets and eight confirmed ones that might be able to host life.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHubble telescope snaps new images of iconic stellar nursery
Hubble's new view of the Pillars of Creation, a star-forming region in the Milky Way, hints at how the nebula has changed over the last 20 years.