Astronomy
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyAstronomers may not have found a sign of the universe’s first stars after all
A new study of radio waves from early in the universe’s history finds no hint of the “cosmic dawn” claimed by an earlier study.
-
 Space
SpaceHow Russia’s war in Ukraine hinders space research and exploration
A Mars rover, an X-ray telescope and several low-Earth satellites are at risk in response to international sanctions on Russia.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Astronomy
AstronomyA fast radio burst’s unlikely source may be a cluster of old stars
The burst’s origin in a globular cluster suggests that not all these enigmatic blasts come from young stellar populations.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA rare collision of dead stars can bring a new one to life
These carbon- and oxygen-covered stars may have formed from an unusual merging of two white dwarfs.
By Nikk Ogasa -
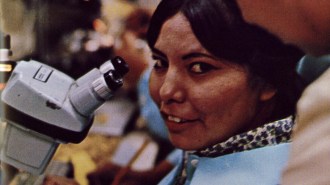 Computing
ComputingCore memory weavers and Navajo women made the Apollo missions possible
The stories of the women who assembled integrated circuits and wove core memory for the Apollo missions remain largely unknown.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHow ‘hot Jupiters’ may get their weirdly tight orbits
Gravitational kicks from other planets and stars can send giant worlds into orbits that bring them close to their suns.
By Ken Croswell -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThese are the first visible-light images of Venus’ surface captured from space
Cameras aboard NASA’s Parker Solar Probe managed to peer through Venus’ thick clouds to photograph the planet’s surface.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Space
SpaceThe heart of the Milky Way looks like contemporary art in this new radio image
The MeerKAT telescope array in South Africa provided this image of radio emissions from the center of our galaxy using data taken over three years.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe James Webb Space Telescope has reached its new home at last
The most powerful telescope ever launched still has a long to-do list before it can start doing science.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyAn X-ray glow suggests black holes or neutron stars fuel weird cosmic ‘cows’
With the brightest X-ray glow of a new class of exploding stars, cosmic oddity AT2020mrf boosts evidence of these mysterious blasts’ power source.
By Liz Kruesi -
 Astronomy
AstronomyAn early outburst portends a star’s imminent death
An eruption before a stellar explosion was the first early warning sign for a standard type of supernova.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyAstronomers identified a second possible exomoon
Kepler 1708 b i, a newly discovered candidate for an exoplanet moon, has a radius about 2.6 times that of Earth, a new study suggests.
By Sid Perkins