Animals
-
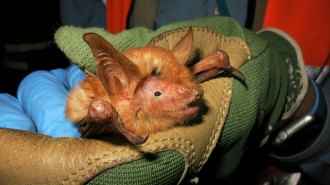 Animals
AnimalsA new orange and black bat species is always ready for Halloween
A new species from the sky islands of Africa’s Nimba Mountains shows bats’ colorful streak.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeGiant worms may have burrowed into the ancient seafloor to ambush prey
20-million-year-old tunnels unearthed in Taiwan may have been home to creatures that ambushed prey similar to today’s monstrous bobbit worms.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome bacteria are suffocating sea stars, turning the animals to goo
For years, researchers thought an infectious pathogen was behind sea star wasting disease. Instead, bacteria deplete the starfishes’ oxygen.
-
 Life
LifeMonitor lizards’ huge burrow systems can shelter hundreds of small animals
Two species of Australian monitor lizards dig nests four meters deep. Now scientists reveal that the burrows are home to far more than their creators.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsSome electric eels coordinate attacks to zap their prey
Electric eels were thought be to solitary hunters, until researchers observed over 100 eels hunting together, releasing coordinated electric attacks on corralled prey.
-
 Plants
PlantsRats with poisonous hairdos live surprisingly sociable private lives
Deadly, swaggering rodents purr and snuggle when they’re with mates and young.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNewborn megalodon sharks were larger than most adult humans
Preserved pieces of backbone suggest that megalodon sharks were about 2 meters long at birth.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice may ‘catch’ each other’s pain — and pain relief
Healthy mice mirror a companion’s pain or morphine-induced relief. Disrupting certain connections in the brain turns off such empathetic behaviors.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBrown tree snakes use their tails as lassos to climb wide trees
A never-before-seen climbing technique could inspire the creation of new serpentine robots to navigate difficult terrains.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese spiders may sew leaves into fake shelters to lure frogs to their doom
Madagascar’s huntsman spiders use silk to turn two leaves into a cool hollow. Such microhabitats may appeal to the spiders’ prey, a study suggests.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsRumors of a ‘murder hornet’ apocalypse may have been exaggerated
Murder hornets sightings in the Pacific northwest inspired a mix of concern and delight.
-
 Animals
AnimalsClearing land to feed a growing human population will threaten thousands of species
Changing where, how and what food is grown could largely avoid biodiversity losses, scientists say.