Explore the history of blood from vampires to the ‘Menstrual Man’
Rose George’s book ‘Nine Pints’ offers readers an engaging and insightful cultural and scientific history of blood.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

Mathematical equations describing interactions between wildfires and the air around them help explain their power and destruction.
Rose George’s book ‘Nine Pints’ offers readers an engaging and insightful cultural and scientific history of blood.

Scientists have found a mathematical explanation for the complex patterns on the wings of dragonflies and other insects.

An inexpensive, user-friendly device that’s based on an mbira could help identify counterfeit and contaminated medications.

Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.

New strategies aim to help transplant recipients keep their organs healthy with fewer (or no) immune suppressing drugs.

Scientists are still learning more about the health effects of chemical sweeteners

Simulations suggest that the theoretical substance known as nuclear pasta is 10 billion times as strong as steel.

Honeybees clumped on trees may adjust their positions to keep the cluster together when it’s jostled by wind, a new study suggests.
Killing dormant cells in the brains of mice staved off memory trouble.

Scientists can sleuth out wildlife crime and aid law enforcement by tracing elephant DNA from ivory seizures back to the source.

For the first time, a gene drive caused a population crash of mosquitoes in a small-scale test.
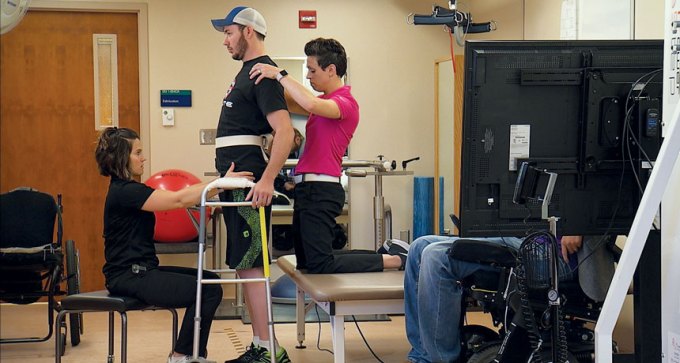
Researchers find success at restoring movement to paralyzed legs, giving hope to people with paraplegia.

Researchers stumbled upon a new species of coral reef fish with spectacular coloration and a unique habitat.
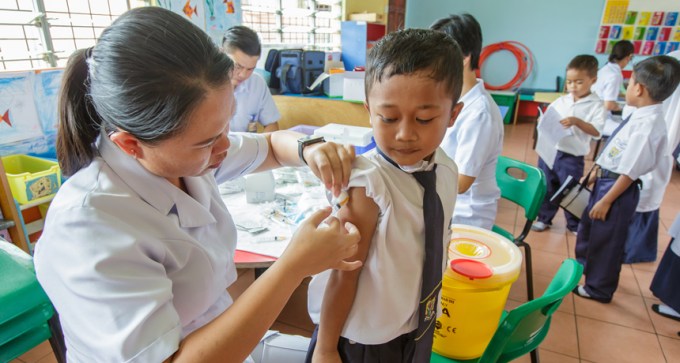
A new vaccine for those infected, but not sick, with tuberculosis reduced new active cases by 54 percent, compared with those given a placebo.
A team of fiberglass-spinning robots could create tubing to help build bridges, buildings or other structures.

Manta rays filter feed differently than other ocean creatures.

A large study of U.S. children ties lots of screen time to lower thinking skills, but the relationship between the two is still unclear.

A large-scale lidar survey of Guatemalan forests reveals evidence of ancient, interconnected Maya cities.

A new calculation says SETI searches have combed the equivalent of a hot tub out of Earth’s oceans looking for extraterrestrial intelligence in space.

Signals from the ANITA experiment don’t square with the properties of elementary particles cataloged in the standard model.

CRISPR/Cas9 replays domestication to make better ground cherries and tomatoes.
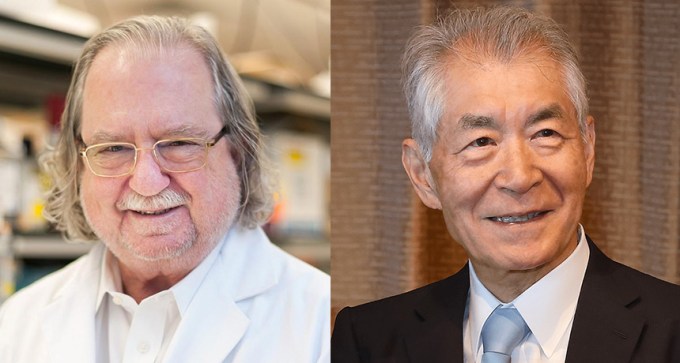
Two scientists share the 2018 medicine Nobel for identifying proteins that act as brakes on tumor-fighting T cells.

The 2018 Nobel Prize in physics went to scientists — including the third-ever female winner — who made optical tweezers and boosted the strength of laser pulses.

Africa’s tallest creatures get their characteristic patterns of spots from their moms, a new study finds.

A single sighting with the Hubble Space Telescope seems to confirm that there’s a Neptune-sized moon orbiting exoplanet Kepler 1625b.

The three winners, which include the fifth woman to win the chemistry prize, pioneered techniques used to fashion customized proteins for new biofuels and drugs.
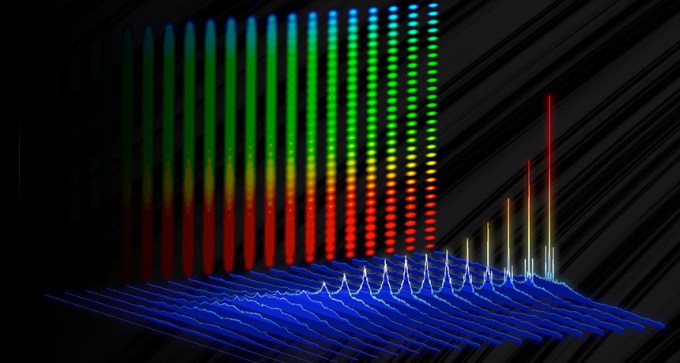
A new technique allows lasers to pulsate at a higher rate than ever before.

A new report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change compares the impact of warming targets on extreme weather, sea level rise and habitat loss.

Climate change and tech innovations inspired the new Nobel Memorial Prize winners in Economic Sciences.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address to access the digital replica edition.