Music soothes the aging brain in film ‘Alive Inside’
A social worker highlighted in a new documentary goes on a quest to bring tunes to nursing homes.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

A social worker highlighted in a new documentary goes on a quest to bring tunes to nursing homes.
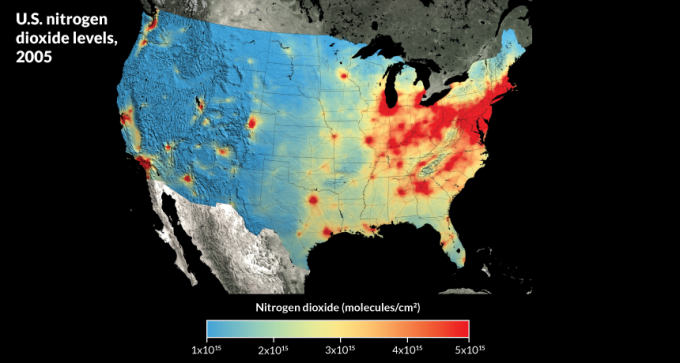
Satellite views reveal good news on U.S. air pollution trends.

A genetic survey reveals that African elephants harbor more smell sensors than any other known animal.

Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
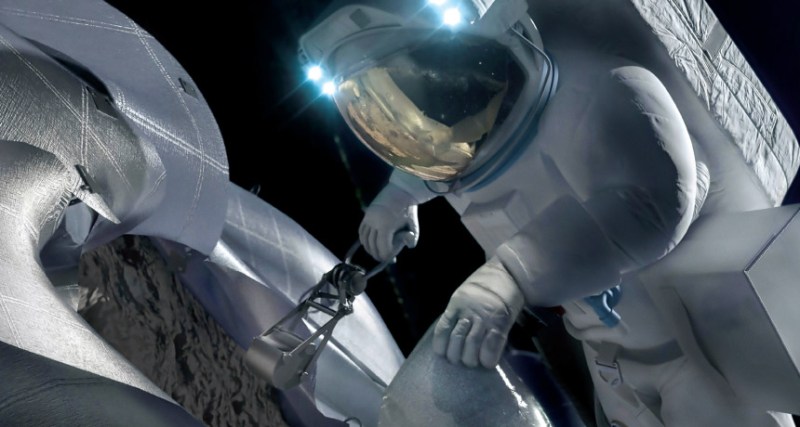

NASA wants to bag an asteroid using robotic arms or an enormous sack and place the rock in the moon’s orbit for study. This may keep astronauts working but not, as NASA claims, get them Mars-ready.

A relatively mild treatment involving radiation and chemo followed by a bone marrow transplant may treat sickle cell disease in adults.

Specialized cells in the retina separate different wavelengths of light to enable sharp vision during the day without harming night vision.

Mild defects in embryonic cells could explain physical similarities along with tameness across domesticated species.

Two scientists argue that Voyager 1 space probe is still in solar bubble, despite NASA’s announcements to the contrary.

Misfolded proteins, the hallmark of Alzheimer’s and mad cow diseases, are found in urine of women with preeclampsia.

A group of Homo sapiens left footprints about 36,500 years ago, not 15,000 as scientists had thought.
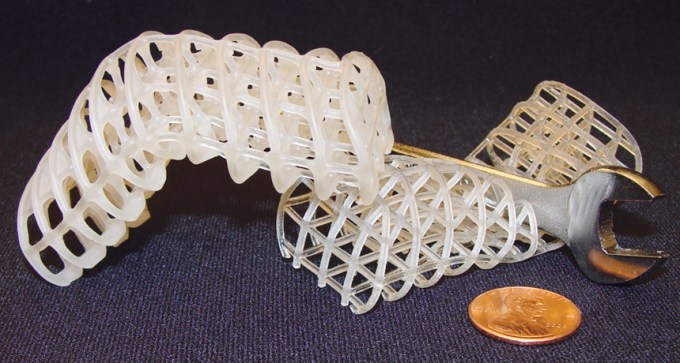
Heat-controlled materials could serve as skeleton for shape-shifting robots.
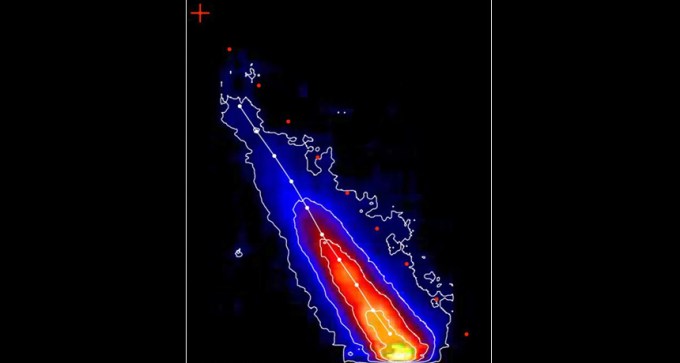
Comet ISON disintegrated at least eight hours before it grazed the surface of the sun last fall, new observations show.

Lasting sandstone structures form when weighed-down sand locks into stable formations, researchers find in laboratory experiment.

To locate invasions, termite soldiers listen for millisecond-long delays in vibrational distress signals sent out by other soldiers.
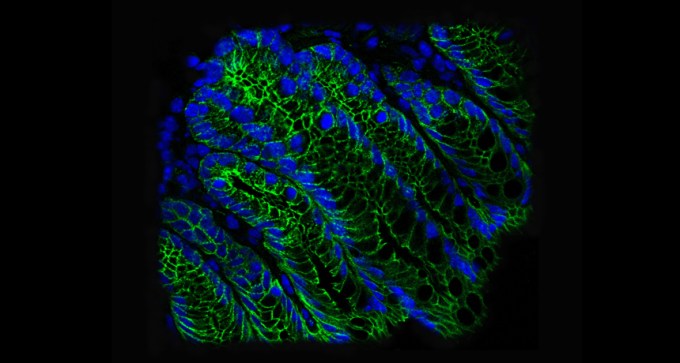
Western nations experience high levels of colon cancer, and carbo-loading gut microbes might explain why, says a new study in mice.

From thousands of genomes, researchers pinpoint dozens of DNA changes that may underlie schizophrenia

Mouse sperm hunt for eggs in packs, but grouping doesn’t boost speed. Instead, gangs of the reproductive cells move in straighter lines.

Saliva from moose and reindeer sabotages plants’ chemical weaponry.

Topological insulators could speed up how computers switch between 1s and 0s.
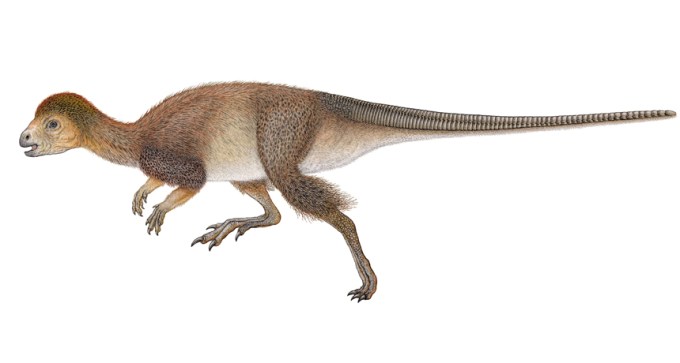
Newly discovered fossil suggests feathers may have been common among all dinosaur species.

Organic compound could cull valuable xenon from the air and detect cancer-causing radon in homes.

Primates near the ill-fated nuclear power plant may have been affected by radiation.

Prolonged used of levodopa doesn’t increase the severity of side effects from the Parkinson’s drug, new research shows.

The reconstruction of a massive eruption 4.5 million years ago near Yellowstone National Park suggests that magma chambers merging together beneath a supervolcano can trigger explosions in less than 10,000 years.

Irrigating city parks with recycled water may flood the soil with drug-resistant microbes.

Planet-sterilizing impacts probably snuffed out early life on Earth until around 4.3 billion years ago.

MIT’s Erik and Martin Demaine create puzzle typefaces to test new ideas.

On display for the 100th anniversary of her species’ extinction, the final passenger pigeon specimen looks pretty good.

Experiments in 1964 resulted in “exploding” clouds.

Katherine Freese shares her insights as a scientist studying dark matter and other mysterious components of the universe.
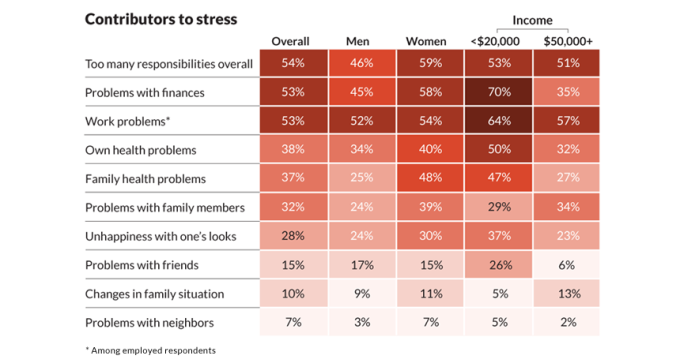
Along with work and other responsibilities, health problems are prominent causes of stress.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address to access the digital replica edition.