Search Results for: mutations
Skip to resultsCan’t find what you’re looking for? Visit our FAQ page.
2,461 results for: mutations
-
 Health & Medicine
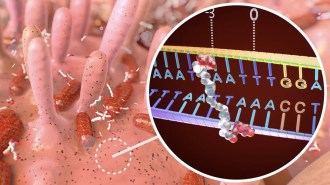
Health & MedicineHow a bacterial toxin linked to colon cancer messes with DNA
A closeup look at colibactin’s structure reveals chemical motifs that guide its mutation-wreaking “warheads” to specific stretches of DNA.
By Elise Cutts -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGum disease bacteria can promote cancer growth in mice
In mice, the oral bacteria F. nucleatum can travel to mammary tissue via the bloodstream, where it can damage healthy cells.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFinding immune cells that stop a body from attacking itself wins medicine Nobel
Shimon Sakaguchi discovered T-reg immune cells. Mary Brunkow and Fred Ramsdell identified the cells’ role in autoimmune disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s how air pollution may trigger lung cancer
Exposure to air pollution may trigger DNA mutations that cause lung cancer in nonsmokers.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsAI tool AlphaGenome predicts how one typo can change a genetic story
The tool helps scientists understand how single-letter mutations and distant DNA regions influence gene activity, shaping health and disease risk.
-
 Life
LifeHorses may have become rideable with the help of a genetic mutation
To make horses rideable during domestication, people may have inadvertently targeted a mutation in horses to strengthen their backs and their balance.
By Jake Buehler -
 Genetics
GeneticsGenetics reveal the origin story of East Asia’s favorite sweet bean
The origin of red beans — also called adzuki — has been murky. A new study says Japan is where it all started.
By Celina Zhao -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePersonalized gene editing saved a baby, but the tech’s future is uncertain
The personalized CRISPR treatment could be the future of gene therapy, but hurdles remain before everyone has access.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThese medical breakthroughs and advances gave patients new hope in 2025
Advances delivered what may feel like medical miracles, including the first bladder transplant, a lifesaving personalized gene therapy and more.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsSpider silk-making organs evolved due to a 400-million-year-old genetic oops
An ancient ancestor of spiders and relatives doubled its genome about 400 million years ago, setting the stage for the evolution of spinnerets.
By Jake Buehler -
 Plants
PlantsA leaf’s geometry determines whether it falls far from its tree
Shape and symmetry help determine where a leaf lands — and if the tree it came from can recoup the leaf’s carbon as it decomposes.
-
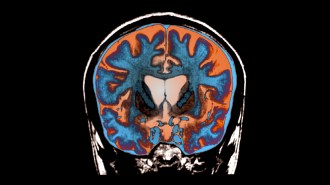 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn a first, Huntington’s disease is slowed by an experimental treatment
An experimental gene therapy slowed Huntington’s by up to 75 percent in a small clinical trial. While not a cure, it may give patients longer lives.