Search Results for: Virus
Skip to resultsCan’t find what you’re looking for? Visit our FAQ page.
6,291 results for: Virus
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySpeeding up the evolution of proteins wins the chemistry Nobel
Work on evolving new proteins from old ones takes the Nobel Prize in chemistry.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe CDC says 80,000 people died from the flu last year
The 2017-2018 flu season was one of the deadliest on record for the United States.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySpeeding up evolution to create useful proteins wins the chemistry Nobel
The three winners, which include the fifth woman to win the chemistry prize, pioneered techniques used to fashion customized proteins for new biofuels and drugs.
By Laurel Hamers and Maria Temming -
 Physics
PhysicsGroundbreaking ways of manipulating light win trio the 2018 physics Nobel
Three scientists, including the third woman to win a physics Nobel, are honored for their laser inventions.
-
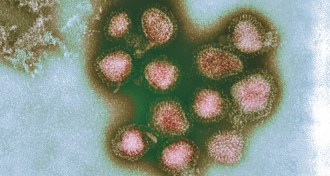 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, a flu pandemic spurred vaccine research
A half-century after the Hong Kong flu pandemic, scientists are getting closer to a universal vaccine.
-
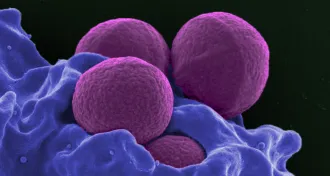 Genetics
GeneticsSmuggling a CRISPR gene editor into staph bacteria can kill the pathogen
A new way fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria co-opts toxin-producing genes.
-
 Physics
PhysicsDazzling laser feats earn these physicists a Nobel
The 2018 Nobel Prize in physics went to scientists — including the third-ever female winner — who made optical tweezers and boosted the strength of laser pulses.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLisa Manning describes the physics of how cells move
Physicist Lisa Manning probes how physical forces influence cell behavior in asthma and other conditions.
-
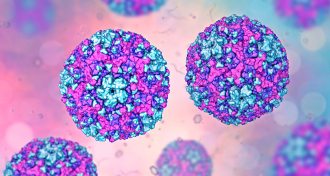 Life
LifeWe may now know when hand, foot and mouth disease outbreaks will occur
Birthrates and immunity rates predict the spread of viruses that cause hand, foot and mouth disease.
-
 Life
LifeHow to make organ transplants last
New strategies aim to help transplant recipients keep their organs healthy with fewer (or no) immune suppressing drugs.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyBefore it burned, Brazil’s National Museum gave much to science
When Brazil’s National Museum went up in flames, so did the hard work of the researchers who work there.
-
 Oceans
OceansViruses may help phytoplankton make clouds — by tearing the algae apart
Sick phytoplankton shed their calcium carbonate plates more easily than their healthy counterparts, which could play a role in forming clouds.