Search Results for: Dolphins
Skip to resultsCan’t find what you’re looking for? Visit our FAQ page.
459 results for: Dolphins
-
 Animals
Animals‘Wonderful nets’ of blood vessels protect dolphin and whale brains during dives
Complex networks of blood vessels called retia mirabilia that are associated with cetaceans’ brains and spines have long been a mystery.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhy traumatic brain injuries raise the risk of a second, worse hit
Recent hits to Miami Dolphins quarterback Tua Tagovailoa have reignited discussions of brain safety for professional football players. Brain experts weigh in.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyTina Lasisi wants to untangle the evolution of human hair
Tina Lasisi is pioneering studies of human variation in an ethical and scientifically sound way.
By Aina Abell -
 Climate
ClimateHow Kenyans help themselves and the planet by saving mangrove trees
Communities in Kenya took action to restore their coastal mangrove forests, reaping economic and environmental benefits. Others are following suit.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese dolphins may turn to corals for skin care
For Indo-Pacific bottlenosed dolphins, rubbing against corals and sea sponges that contain antibacterial compounds could help keep skin healthy.
-
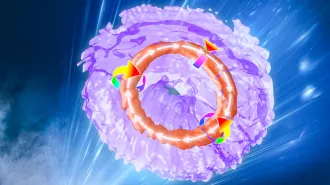 Physics
PhysicsScientists created ‘smoke rings’ of light
A swirling doughnut of light shows that vortex rings aren’t just for fluids anymore.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a western banded gecko eats a scorpion
New high-speed video details how usually mild-mannered geckos shake and incapacitate their venomous prey.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFemale dolphins have a clitoris much like humans’
The similarities suggest female dolphins experience sexual pleasure, which may explain why the species is so randy all the time.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPolar bears sometimes bludgeon walruses to death with stones or ice
Inuit reports of polar bears using tools to kill walruses were historically dismissed as stories, but new research suggests the behavior does occur.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCapturing the sense of touch could upgrade prosthetics and our digital lives
Haptics researchers are working on ways to add touch to virtual reality, online shopping, telemedicine and advanced artificial limbs.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHaving more friends may help female giraffes live longer
A more gregarious life, even while just munching shrubbery, might mean added support and less stress for female giraffes.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsNaked mole-rat colonies speak with unique dialects
Machine learning reveals that these social rodents communicate with distinctive speech patterns that are culturally inherited.