Pneumonia bacteria attacks lungs with toxic weaponry
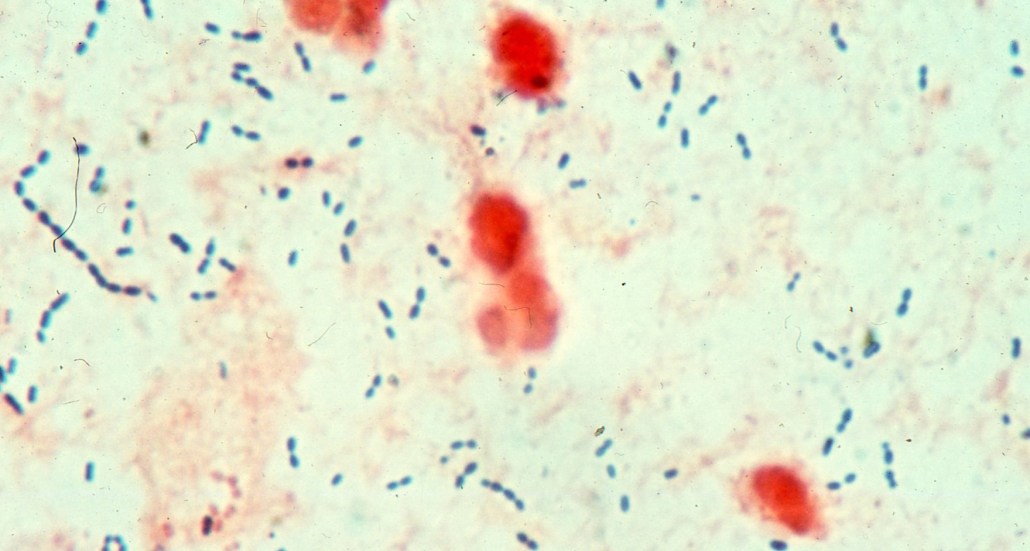
Streptococcus pneumoniae attack cells and genes in the lungs using hyrdogen peroxide, a new study finds.
Microbe World/Flickr (CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)

Streptococcus pneumoniae attack cells and genes in the lungs using hyrdogen peroxide, a new study finds.
Microbe World/Flickr (CC BY-NC-SA 2.0)