
Senior writer Tina Hesman Saey is a geneticist-turned-science writer who covers all things microscopic and a few too big to be viewed under a microscope. She is an honors graduate of the University of Nebraska-Lincoln where she did research on tobacco plants and ethanol-producing bacteria. She spent a year as a Fulbright scholar at the Georg-August University in Göttingen, Germany, studying microbiology and traveling. Her work on how yeast turn on and off one gene earned her a Ph.D. in molecular genetics at Washington University in St. Louis. Tina then rounded out her degree collection with a master’s in science journalism from Boston University. She interned at the Dallas Morning News and Science News before returning to St. Louis to cover biotechnology, genetics and medical science for the St. Louis Post-Dispatch. After a seven year stint as a newspaper reporter, she returned to Science News. Her work has been honored by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine, the Endocrine Society, the Genetics Society of America and by journalism organizations.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Tina Hesman Saey
-
 Health & Medicine
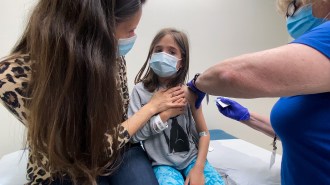
Health & MedicinePfizer says its COVID-19 vaccine is safe and works well for kids ages 5–11
A lower dose of the vaccine produced as many antibodies in elementary school–age kids as a full-dose shot did in teens and young adults.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew studies hint that the coronavirus may be evolving to become more airborne
More coronavirus RNA is in fine aerosols than in larger droplets, but masks can reduce the amount of virus in the air.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSchools are reopening. COVID-19 is still here. What does that mean for kids?
Children do get COVID-19, and some become very sick and even die. But the disease’s long-term effects on kids remain uncertain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew delta variant studies show the pandemic is far from over
The coronavirus’s delta variant is different from earlier strains of the virus in worrying ways, health officials are discovering.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy the CDC says it’s crucial to start wearing masks indoors again
While unvaccinated people are driving the spread of the coronavirus, vaccinated people infected with the delta variant may also easily transmit it.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy it’s still so hard to find treatments for early COVID-19
Small studies, unexpected side effects and incomplete information about how drugs work can stymie clinical trials for drugs that can treat COVID-19.
-
 Humans
HumansOnly a tiny fraction of our DNA is uniquely human
Some of the exclusively human tweaks to DNA may have played a role in brain evolution.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow your DNA may affect whether you get COVID-19 or become gravely ill
A study of 45,000 people links 13 genetic variants to higher COVID-19 risks, including a link between blood type and infection and a newfound tie between FOXP4 and severe disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
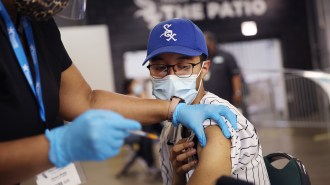
Health & MedicineThe benefits of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines outweigh the risk of rare heart inflammation
A CDC group says the benefits of the Pfizer and Moderna shots outweigh the risk of myocarditis and pericarditis in adolescents and young adults.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what we know about the risks of serious side effects from COVID-19 vaccines
Allergic reactions, blood clots and possibly heart problems are rare and their risks don’t outweigh the benefits of getting vaccinated, experts say.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA gene-based therapy partially restored a blind man’s vision
Light-activated proteins inserted in eye nerve cells and special goggles help the man, who lost his sight due to retinitis pigmentosa, see objects.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe CDC’s changes to mask guidelines raised questions. Here are 6 answers
Experts weigh in on the U.S. CDC’s recommendation fully vaccinated individuals removing masks indoors and what it means for the pandemic’s future.