
Nikk Ogasa is a staff writer who focuses on the physical sciences for Science News, based in Tucson, Arizona. He has a master's degree in geology from McGill University, where he studied how ancient earthquakes helped form large gold deposits. He earned another master's degree in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz. His stories have been published in Science, Scientific American, Mongabay and the Mercury News, and he was the summer 2021 science writing intern at Science News.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Nikk Ogasa
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceJupiter’s lightning bolts contort the same way as Earth’s
Jovian lightning extends in jagged steps as it does on Earth, data from NASA’s Juno spacecraft suggest. The finding might aid the search for life.
-
 Tech
TechDeblina Sarkar is building microscopic machines to enter our brains
The ultratiny devices can communicate wirelessly from inside living cells and may one day help cure brain diseases.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSaturn’s rings may be no more than 400 million years old
An analysis of data from NASA’s defunct Cassini probe suggests Saturn's rings materialized more than 100 million years after trilobites appeared on Earth.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentMore than half of the world’s largest lakes are drying up
Satellite data from 1992 to 2020 reveal that 53 percent of the world’s largest freshwater bodies shrank during that period while only 24 percent grew.
-
 Climate
ClimateThawing permafrost may unleash industrial pollution across the Arctic
As the frozen ground warms due to climate change, industrial pollutants could flow free from thousands of sites across the Arctic.
-
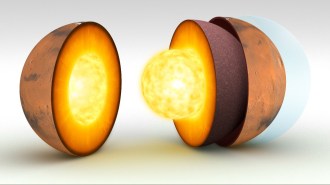 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSeismic waves crossing Mars’ core reveal details of the Red Planet’s heart
NASA’s InSight lander observed a quake and an impact on the farside of Mars, allowing researchers to measure physical properties of the planet’s core.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceBaby Jupiter glowed so brightly it might have desiccated its moon
During its infancy, Jupiter may have glowed about 10 thousand times brighter than it does today, which may explain why its moon Io is completely dry.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureMartian soil may have all the nutrients rice needs
Experiments hint that in the future, we might be able to grow the staple food in the soils of the Red Planet.
-
 Earth
EarthA moon-forming cataclysm could have also triggered Earth’s plate tectonics
Deeply buried remnants of a hypothetical planet that slammed into Earth 4.5 billion years ago might have set subduction into motion.
-
 Climate
ClimateWildfires in boreal forests released a record amount of CO2 in 2021
Boreal forests store about one-third of the world’s land-based carbon. With wildfires increasing there, fighting climate change could get even harder.
-
 Climate
ClimateAn incendiary form of lightning may surge under climate change
Relatively long-lived lightning strikes are the most likely to spark wildfires and may become more common as the climate warms.
-
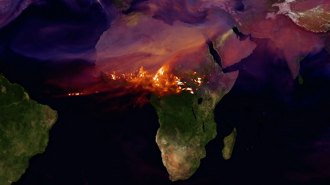 Climate
ClimateClimate ‘teleconnections’ may link droughts and fires across continents
Far-reaching climate patterns like the El Niño-Southern Oscillation may synchronize droughts and regulate scorching of much of Earth’s burned area.