
Meghan Rosen is a senior writer who reports on the life sciences for Science News. She earned a Ph.D. in biochemistry and molecular biology with an emphasis in biotechnology from the University of California, Davis. Her dissertation work involved studying mutated proteins in liver and kidney cancer. She later graduated from the science communication program at UC Santa Cruz. Prior to joining Science News in 2022, she was a media relations manager at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Her work has appeared in Wired, Science, and The Washington Post, among other outlets. Once for McSweeney’s, she wrote about her kids’ habit of handing her trash, a story that still makes her (and them) laugh.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Meghan Rosen
-
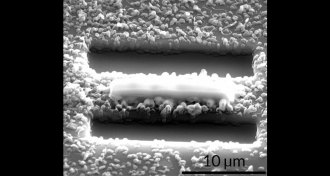 Chemistry
Chemistry‘Q-carbon’ may offer quick route to diamonds
Q-carbon might be the third form of solid carbon, but some scientists have doubts.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyLong-necked monsters roamed more than Scotland’s lochs
The discovery of sauropod footprints in Scotland suggest the dinosaurs lived in lagoons.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCan DNA predict a face?
DNA-based facial sketches are moving into the crime-solving arena. With current science, predictions of some features are better than others.
-
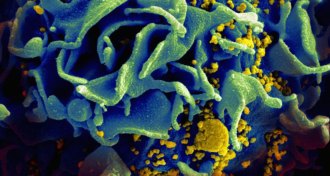 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTaking antiviral drug ‘on demand’ can guard against HIV
The antiviral drug Truvada taken before and after sex cuts HIV transmission rates.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTaking antiviral drug ‘on demand’ guards against HIV
The antiviral drug Truvada taken before and after sex cuts HIV transmission rates.
-
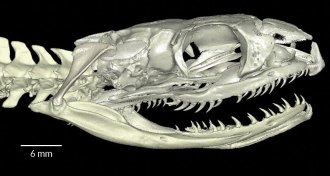 Animals
AnimalsSnakes evolved from burrowing ancestor, new data suggest
A new X-ray analysis of inner ears is the latest to weigh in on whether modern snakes descended from a burrowing or a swimming reptile.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHaving parasites can boost fertility
Infection with parasitic worms tinkers with fertility.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePutting the big chill on cryotherapy
Evidence is lacking for whole-body cryotherapy as a treatment for muscle soreness.
-
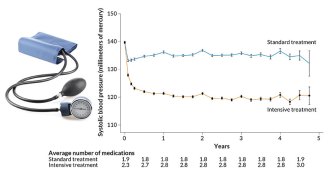 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDropping blood pressure to 120 lowers heart woes, data confirm
Aggressive treatment to lower systolic blood pressure to 120 reduces risk of heart attack, but causes some side effects.
-
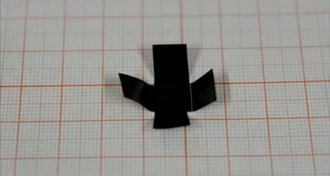 Tech
TechLaser light turns graphene paper into a microbot
Tiny origami-inspired robot uses laser light to walks like an inchworm.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDiagram captures microbes’ influence across animal kingdom
A network diagram of animal species shows that many microbes living in humans also make themselves at home in dogs, pigs and cattle.
-
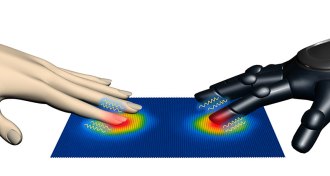 Tech
TechElectronic skin feels the heat, hears the sound
Electronic skin inspired by human fingertips detects texture, pressure, heat and sound.