
Erin Garcia de Jesús is a staff writer at Science News. She holds a Ph.D. in microbiology from the University of Washington, where she studied virus/host co-evolution. After deciding science as a whole was too fascinating to spend a career studying one topic, she went on to earn a master’s in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz. Her writing has appeared in Nature News, Science, Eos, Smithsonian Voices and more, and she was the winter 2019 science writing intern at Science News.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Erin Garcia de Jesús
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what you need to know about COVID’s XBB.1.5 ‘Kraken’ variant
XBB.1.5, an offshoot of the coronavirus’s omicron variant, can hide from parts of the immune system, but vaccines and some treatments still work.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyKatydids had the earliest known insect ears 160 million years ago
Fossils from the Jurassic Period show katydid ears looked identical to those of modern katydids and could pick up short-range calls.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineViruses other than the coronavirus made headlines in 2022
Here’s the latest on monkeypox, Ebola, bird flu and other outbreaks that hit this year.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, a ‘cure’ for intoxication showed promise
In 1972, vitamin and chemical injections reduced the amount of time that rats fed alcohol spent drunk. The science has yet to pan out for people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis child was treated for a rare genetic disease while still in the womb
Babies born with infantile-onset Pompe disease typically have enlarged hearts and weak muscles. But 1-year-old Ayla has a normal heart and walks.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA swarm of sneaky omicron variants could cause a COVID-19 surge this fall
Scientists are tracking similar mutations showing up in many variants that help the coronavirus evade some of our immune defenses and treatments.
-
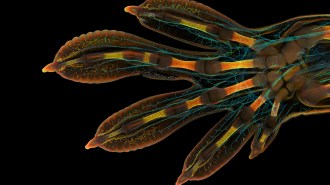 Life
LifeA glimpse inside a gecko’s hand won the 2022 Nikon Small World photo contest
The annual competition highlights microscopic images that bring the smallest details from science and nature to life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Breathless’ explores COVID-19’s origins and other pandemic science
In his new book, David Quammen examines what we’ve learned about SARS-CoV-2 and puts the pandemic in the context of previous coronavirus scares.
-
 Earth
Earth50 years ago, scientists dug into Pangaea’s past lives
In 1972, scientists wondered whether Pangaea was Earth’s only supercontinent. Fifty years later, we know it wasn’t the first and it won’t be the last.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine5 people with lupus are in remission after CAR-T cell treatment
More than six months after CAR-T cell treatment, five patients are in remission and have functional immune systems.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePoliovirus is spreading in New York. Here’s what you need to know
With signs of poliovirus spreading in a handful of counties in New York, unvaccinated people could be at risk of paralytic polio.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNeed to keep cockatoos out of your trash? Try bricks, sticks or shoes
In Sydney, humans may be in an escalating arms race with cockatoos. People are trying new tools to keep the pesky parrots out of their trash.