
Senior physics writer Emily Conover joined Science News in 2016. She has a Ph.D. in physics from the University of Chicago, where she studied the weird ways of neutrinos, tiny elementary particles that can zip straight through the Earth. She got her first taste of science writing as a AAAS Mass Media Fellow for the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. She has previously written for Science Magazine and the American Physical Society. She is a two-time winner of the D.C. Science Writers’ Association Newsbrief award, and a winner of the Acoustical Society of America’s Science Communication Award.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Emily Conover
-
 Physics
PhysicsVirgo detector joins LIGO in the search for gravitational waves
The Virgo detector near Pisa, Italy, has begun searching for subtle ripples in the fabric of spacetime.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceDiamond joins the realm of 2-D thin films, study suggests
Scientists squeezed graphene sheets into diamondene.
-
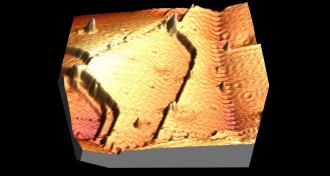 Materials Science
Materials ScienceThe thinnest films of copper look flat, but they aren’t
It turns out that thin films of copper don’t lay flat, a discovery that has implications for computers and handheld electronics.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum tunneling takes time, new study shows
A new measurement disfavors the idea that electrons can escape atoms instantaneously.
-
 Astronomy
Astronomy‘Making Contact’ chronicles an astronomer’s struggle to find E.T.
For decades, astronomer Jill Tarter led the hunt for extraterrestrial intelligence, as detailed in a new biography.
-
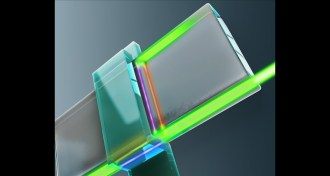 Physics
PhysicsMajorana fermion detected in a quantum layer cake
Scientists found evidence of a particle that is its own antiparticle.
-
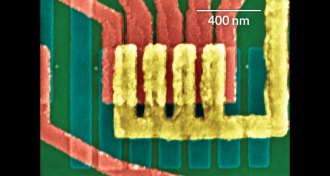 Tech
TechThe incredible shrinking transistor just got smaller
Tiniest transistor, made with carbon nanotubes, suggests computers aren’t done shrinking down.
-
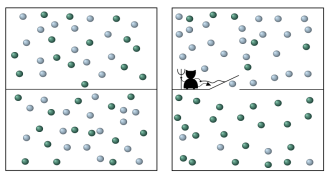 Physics
PhysicsScientists peek inside the mind of Maxwell’s demon
Scientists probe information retained by Maxwell’s demon.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyTeeny-weeny star vies for title of smallest known
A Saturn-sized star is one of the smallest yet discovered.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyTeensy star vies for title of smallest known
A Saturn-sized star is one of the smallest yet discovered.
-
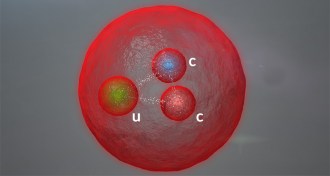 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsNewfound particle relies on its charm(s)
First-of-its-kind subatomic particle is composed of two charm quarks and an up quark.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsChina’s quantum satellite adds two new tricks to its repertoire
Satellite performs quantum teleportation and securely transmits encryption keys.