
Carolyn Gramling is the Earth & Climate writer at Science News. Previously she worked at Science magazine for six years, both as a reporter covering paleontology and polar science and as the editor of the news in brief section. Before that she was a reporter and editor at EARTH magazine. She has bachelor’s degrees in Geology and European History and a Ph.D. in marine geochemistry from MIT and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. She’s also a former Science News intern.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Carolyn Gramling
-
 Earth
EarthTowering fire-fueled thunderclouds can spew as many aerosols as volcanic eruptions
A massive plume of smoke lofted into the stratosphere during Australia’s fires may represent a new class of “volcanic-scale” pyrocumulonimbus clouds.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyHow massive long-necked dinosaurs rose to rule the Jurassic herbivores
New dinosaur fossil dates to same time as a volcanic surge, suggesting ensuing changes in plant life allowed these long-necked giants to emerge.
-
 Climate
ClimateOnce hurricanes make landfall, they’re lingering longer and staying stronger
Warmer ocean waters due to human-caused climate change can help power hurricanes’ fury even after they roar ashore.
-
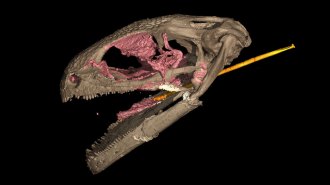 Life
LifeAn ancient amphibian is the oldest known animal with a slingshot tongue
A tiny amphibian that lived 99 million years ago waited for invertebrate prey before snatching them with a swift, shooting tongue.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyBat-winged dinosaurs were clumsy fliers
The two known species of bat-winged dinosaurs were a dead end when it comes to the evolution of bird flight, a new study finds.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyCannibalism in the womb may have helped megalodon sharks become giants
The ancient sea terror Otodus megalodon may have grown to at least 14 meters long thanks to a firstborn pup’s predatory behavior, some researchers say.
-
 Climate
ClimateBy 2100, Greenland will be losing ice at its fastest rate in 12,000 years
The rate of loss of Greenland’s ice will soar over the next century even with greatly reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
-
 Climate
ClimateGlobal warming may lead to practically irreversible Antarctic melting
Simulations suggest that even if the Paris climate goals are met, melting Antarctica ice will still cause sea levels to rise by more than 2 meters.
-
 Oceans
OceansUnderwater earthquakes’ sound waves reveal changes in ocean warming
A new technique uses the echoes of earthquakes in seawater to track the impact of climate change on the oceans.
-
 Earth
EarthEarth’s rarest diamonds form from primordial carbon in the mantle
Chemical analyses of the rarest diamonds suggest the planet’s carbon cycle may not go as deep as scientists thought.
-
 Climate
ClimateNew maps show how warm water may reach Thwaites Glacier’s icy underbelly
New seafloor maps around Thwaites Glacier in Antarctica reveal how deep channels could help warm ocean water melt the glacier from below.
-
 Climate
ClimateBering Sea winter ice shrank to its lowest level in 5,500 years in 2018
Peat cores that record five millennia of climate shifts in the Arctic region suggest recent ice loss is linked to rising carbon dioxide levels.