
Biomedical writer Aimee Cunningham is on her second tour at Science News. From 2005 to 2007, she covered chemistry, environmental science, biology and materials science for Science News. Between stints Aimee was a freelance writer for outlets such as NPR and Scientific American Mind. She has a degree in English from the University of Michigan and a master’s degree in science journalism from New York University. She received the 2019 Award for Excellence in Science and Medical Journalism from the Endocrine Society for the article "Hormone replacement makes sense for some menopausal women."

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Aimee Cunningham
-
 Health & Medicine
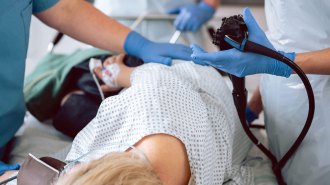
Health & MedicineA study questioning colonoscopy screening’s benefits has big caveats
The study included a lot of people who were invited to get the procedure but didn’t. That’s one limitation of several.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLosing amphibians may be tied to spikes in human malaria cases
Missing frogs, toads and salamanders may have led to more mosquitoes and potentially more malaria transmission, a study in Panama and Costa Rica finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGenetics of human evolution wins 2022 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine
By figuring out how to extract DNA from ancient bones, Svante Pääbo was able to decipher the genomes of our hominid relatives.
-
 Health & Medicine
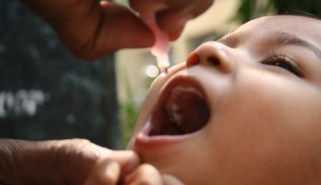
Health & MedicinePoliovirus is spreading in New York. Here’s what you need to know
With signs of poliovirus spreading in a handful of counties in New York, unvaccinated people could be at risk of paralytic polio.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow the COVID-19 pandemic may leave a long-term imprint on our health
As much as we want to put the pandemic in the rearview mirror, the coronavirus’s impact will remain a feature of many tomorrows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA shot of immune proteins may protect against malaria for months
A monoclonal antibody for malaria passed an early hurdle and now will be tested in children in Africa, who are most at risk of dying from the disease.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘Virology’ ponders society’s relationship with viruses
In a collection of wide-ranging essays, microbiologist Joseph Osmundson reflects on the COVID-19 pandemic and calls for “a new rhetoric of care.”
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePfizer’s and Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccines are OK’d for the youngest kids
Babies, toddlers and preschoolers could begin getting immunized against COVID-19 as early as June 21 in the United States.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineUnexplained hepatitis cases in kids offer more questions than answers
There is a lot that is unclear about the hepatitis that’s impacting several hundred children worldwide, but parents shouldn’t panic.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists were seeking the cause of psoriasis
In the 1970s, scientists found a link between a chemical messenger and psoriasis, a complex inflammatory skin disorder.
-
 Health & Medicine
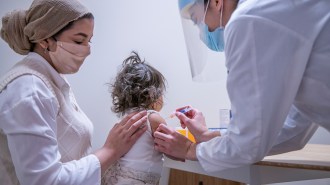
Health & MedicineAntibiotics diminish babies’ immune response to key vaccines
With each round of antibiotics during a child’s first two years, antibody levels to four vaccines dropped further from what’s considered protective.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRacial bias can seep into U.S. patients’ medical notes
Black patients were more often described negatively in medical notes than white patients, which may impact care.