
Biomedical writer Aimee Cunningham is on her second tour at Science News. From 2005 to 2007, she covered chemistry, environmental science, biology and materials science for Science News. Between stints Aimee was a freelance writer for outlets such as NPR and Scientific American Mind. She has a degree in English from the University of Michigan and a master’s degree in science journalism from New York University. She received the 2019 Award for Excellence in Science and Medical Journalism from the Endocrine Society for the article "Hormone replacement makes sense for some menopausal women."

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Aimee Cunningham
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHormone replacement makes sense for some menopausal women
For healthy women within 10 years of menopause, the benefits of hormone therapy for relief of hot flashes or other symptoms may outweigh the risks.
-
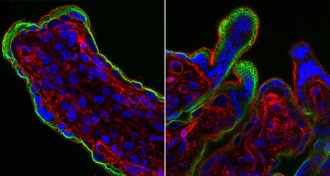 Life
LifeA key virus fighter is implicated in pregnancy woes
In mice, activating a key component of the body’s antiviral machinery in response to a Zika infection can cause harm to developing fetuses.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineU.S. life expectancy drops for the second year in a row
Life expectancy for the U.S. population decreased in 2016, the second year in a row this measure has dropped.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGay, lesbian and bisexual high schoolers report ‘tragically high’ suicide risk
Teens who identify as sexual minorities are more likely to report suicidal behaviors than their heterosexual peers, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFracking linked to low birth weight in Pennsylvania babies
Babies born to moms living within one kilometer of a hydraulic fracturing site were more likely to be born underweight, researchers say.
-
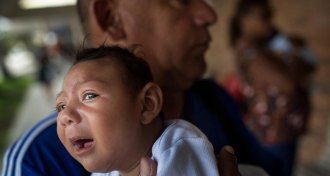 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika cases are down, but researchers prepare for the virus’s return
The number of Zika cases in the Western Hemisphere have dropped this year, but the need for basic scientific and public health research of the virus remains strong.
-
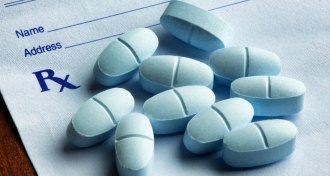 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat hospitals can do to help keep excess opioids out of communities
Guidelines for prescribing opioids following a routine surgery prevented thousands of unnecessary pills from leaving the hospital, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTestosterone may be one reason why men don’t get asthma as much as women
Adult women have higher rates of asthma than men, and testosterone’s effect on the immune system may partly explain that difference.
-
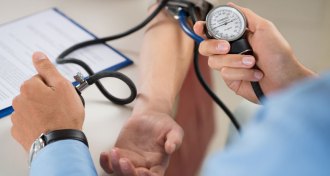 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew blood pressure guidelines put half of U.S. adults in unhealthy range
New hypertension guidelines broaden the range of those considered to have high blood pressure and emphasize lifestyle changes to combat the condition.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCholera pandemics are fueled by globe-trotting bacterial strains
International cholera strains, rather than local ones, have caused raging epidemics, according to research that examined the bacteria’s DNA.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman study supports theory on why dengue can be worse the next time around
The amount of dengue antibodies leftover in the blood may up the chances of a severe second dengue infection, a study finds.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyTrauma surgeon studies gun violence stats — and was one
Joseph Sakran is trying to help counter the U.S. epidemic of gun violence with data.