
Biomedical writer Aimee Cunningham is on her second tour at Science News. From 2005 to 2007, she covered chemistry, environmental science, biology and materials science for Science News. Between stints Aimee was a freelance writer for outlets such as NPR and Scientific American Mind. She has a degree in English from the University of Michigan and a master’s degree in science journalism from New York University. She received the 2019 Award for Excellence in Science and Medical Journalism from the Endocrine Society for the article "Hormone replacement makes sense for some menopausal women."

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Aimee Cunningham
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperts advise: Start colorectal screening at 45, not 50
The American Cancer Society recommends that colorectal screening begin at the age of 45 for average-risk individuals.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFinally, a plan on how to include pregnant women in clinical trials
The FDA is providing initial guidance on how to include pregnant women in clinical trials that study drugs, research that has largely excluded this group in the past.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHurricane Maria killed at least 4,645 people in Puerto Rico, a study estimates
Researchers estimate Puerto Rico’s death toll from Hurricane Maria at more than 4,500 people based on household surveys — dwarfing the official count of 64.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineKeeping people within U.S. blood pressure guidelines saves lives
Big reductions in heart attacks, strokes and deaths may be possible under 2017 blood pressure guidelines.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlack children commit suicide at twice the rate of white kids
The suicide rates for young black kids are higher than those of their white counterparts, a pattern that flips in older kids, researchers find.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese caterpillars march. They fluff. They scare London.
Oak processionary moths have invaded England and threatened the pleasure of spring breezes.
-
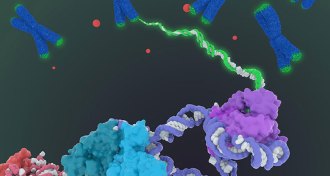 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAn enzyme involved in cancer and aging gets a close-up
The structure of telomerase, described with the greatest detail yet, may give researchers clues to cancer treatments and other telomerase-related illnesses.
-
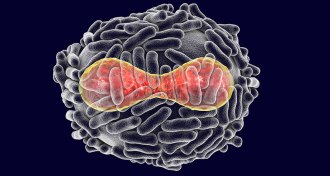 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFDA approves the first smallpox treatment
Concerns about bioterrorism fueled the development of the first treatment for smallpox.
-
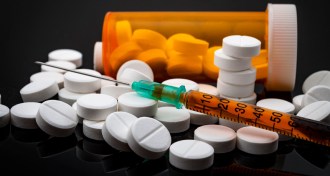 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSynthetic opioids involved in more deaths than prescription opioids
Winning a ghastly contest, synthetic opioids become most common drug involved in U.S. overdose deaths, bypassing prescription opioids in 2016.
-
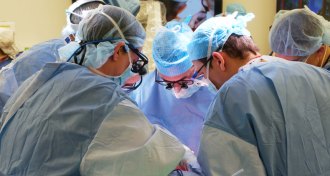 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe first penis-scrotum transplant is the latest to go beyond lifesaving
Advances that give patients new faces, hands and more aim to improve quality of life
-
 Life
LifeLarger spleens may help ‘sea nomads’ stay underwater longer
The Bajau people of Southeast Asia have a gene variant associated with larger spleens, boosting their oxygen while breath-hold diving, researchers say.
-
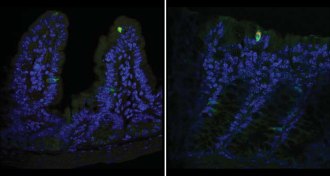 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis is how norovirus invades the body
Norovirus targets a rare type of gut cell, a study in mice finds.