
Biomedical writer Aimee Cunningham is on her second tour at Science News. From 2005 to 2007, she covered chemistry, environmental science, biology and materials science for Science News. Between stints Aimee was a freelance writer for outlets such as NPR and Scientific American Mind. She has a degree in English from the University of Michigan and a master’s degree in science journalism from New York University. She received the 2019 Award for Excellence in Science and Medical Journalism from the Endocrine Society for the article "Hormone replacement makes sense for some menopausal women."

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Aimee Cunningham
-
 Health & Medicine
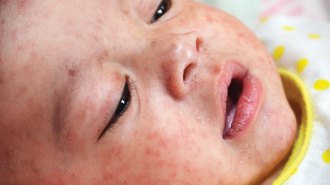
Health & MedicineMeasles got a foothold in the United States this year and almost didn’t let go
Areas of low vaccination are blamed for the United States' largest number of measles cases in more than 25 years.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists’ brains shrank a bit after an extended stay in Antarctica
The experience of an isolated, long-term mission at an Antarctic research station slightly shrunk a part of crew members’ brains, a small study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
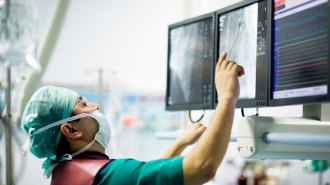
Health & MedicineMedications alone work as well as surgery for some heart disease patients
Patients with stable ischemic heart disease may be able to avoid stents or bypass surgery with medications alone.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDengue cases in the Americas have reached an all-time high
There have been more dengue cases in the Americas this year than ever before, according to the Pan American Health Organization.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFor people with HIV, undetectable virus means untransmittable disease
HIV outreach and care in Washington, D.C., reveals the struggles and successes of getting drugs into the hands of those who need them.
-
 Health & Medicine
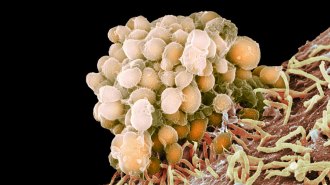
Health & MedicineDrug-resistant microbes kill about 35,000 people in the U.S. per year
The latest CDC report on drug-resistant microbes finds that these pathogens infect close to 3 million people in the United States each year.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVitamin E acetate is a culprit in the deadly vaping outbreak, the CDC says
Researchers detected vitamin E oil in all samples of lung fluid from 29 patients suffering from lung injuries tied to e-cigarettes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new dengue vaccine shows promise — at least for now
The latest vaccine against dengue shows promise in protecting children from the disease, but will need longer term study to ensure kids are safe from future infections.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNearly 1,300 injuries and 29 deaths in the U.S. have been tied to vaping
As the investigation continues, health officials expect multiple causes will be behind the ever-growing number of vaping-related lung injuries.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDiscovery of how cells sense oxygen wins the 2019 medicine Nobel
Understanding the molecular switch that lets cells cope with oxygen has implications for everything from metabolism to wound healing.
-
 Health & Medicine
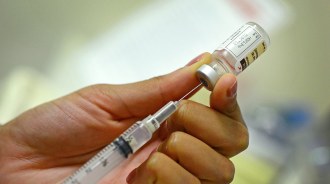
Health & MedicineThe U.S. narrowly eked out a measles win, keeping elimination status
The risk of measles, while low in the United States, still remains due to undervaccinated areas and international travelers importing the virus.
-
 Life
LifeMichelle O’Malley seeks greener chemistry through elusive fungi
Michelle O’Malley studies anaerobic gut fungi, microbes that could help make chemicals and fuels from sustainable sources.