Gene editing creates virus-free piglets
Advance moves the animals one step closer to becoming organ donors for people
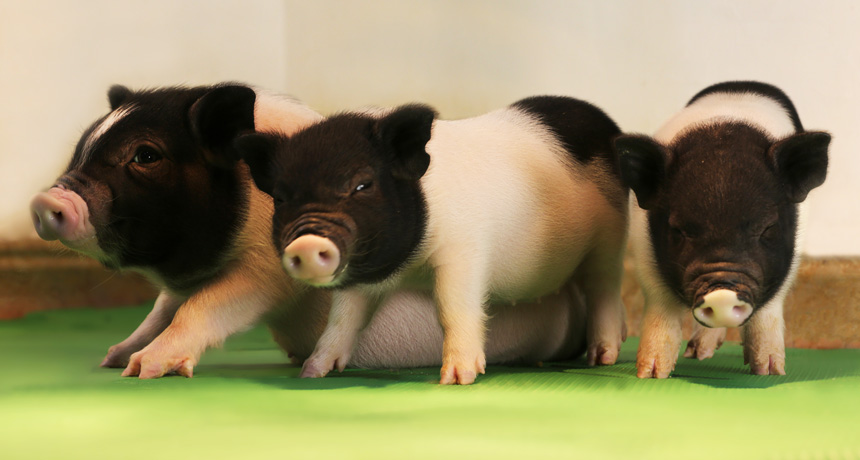

THREE LITTLE PIGS Researchers are working to create pigs that can donate organs for human transplant. These piglets are part of the first litter of pigs engineered to lack viruses called PERVs.
eGenesis