Uncategorized
-
 Health & Medicine
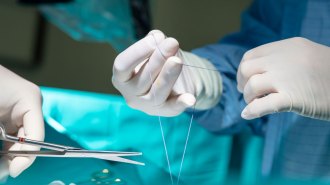
Health & MedicineNew electrical stitches use muscle movement to speed up healing
In rats, the sutures hastened recovery and reduced the risk of infection.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient Scythians had cultural roots in Siberia
A possible sacrificial ritual from around 2,800 years ago suggests mounted herders from Siberia shaped a Eurasian culture thousands of kilometers away.
By Bruce Bower -
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceThe discovery of tools key to machine learning wins the 2024 physics Nobel
John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton used tools from physics to develop data analysis methods that underlie machine learning.
By Emily Conover and Lisa Grossman -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSemaglutide saps mice’s motivation to run
Mice given semaglutide, the key ingredient in drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy, lost weight, but they also voluntarily ran less on a wheel.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBlood pressure may read falsely high if the arm isn’t positioned properly
A clinical trial found blood pressure readings were higher with the arm on the lap or along the side, compared with supported at heart height.
-
 Animals
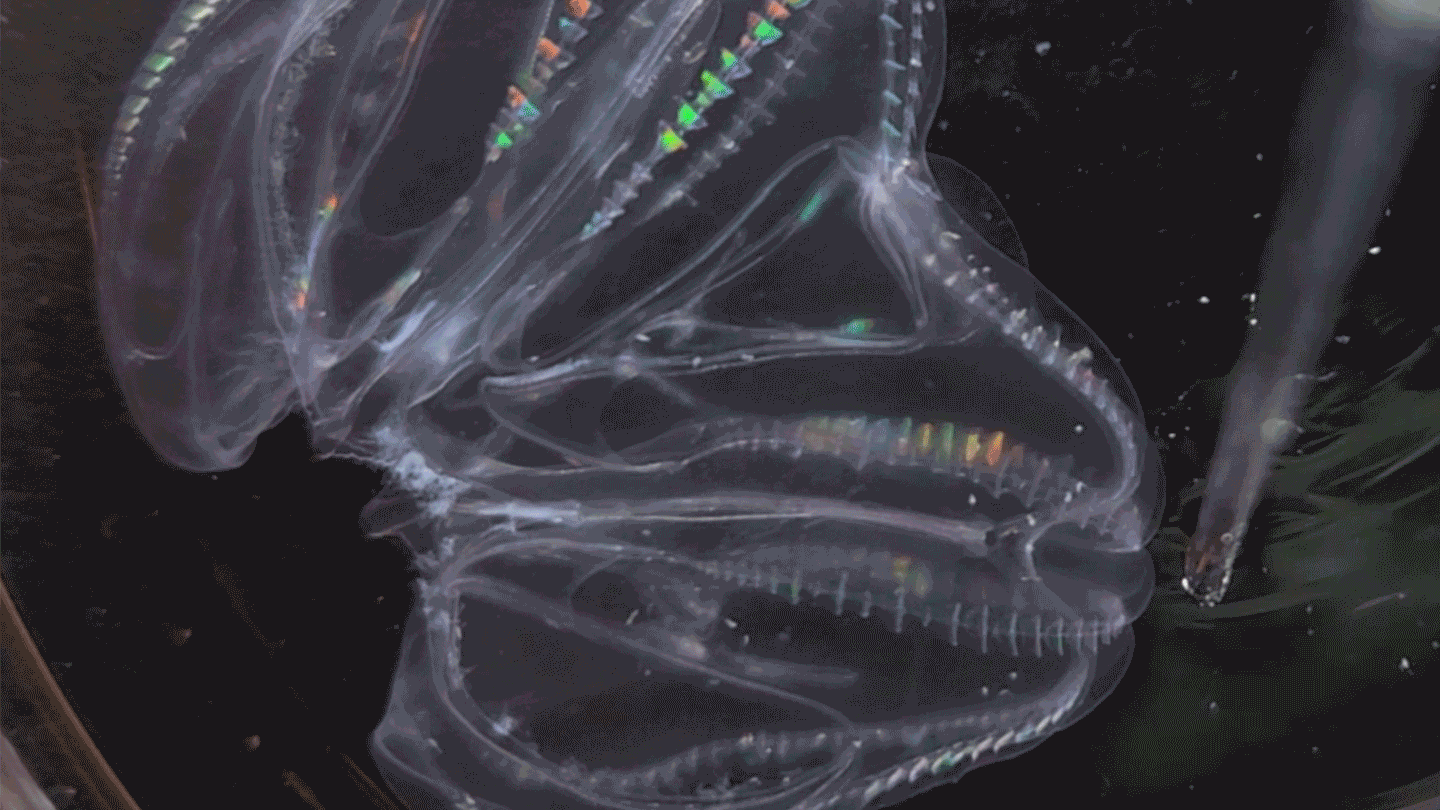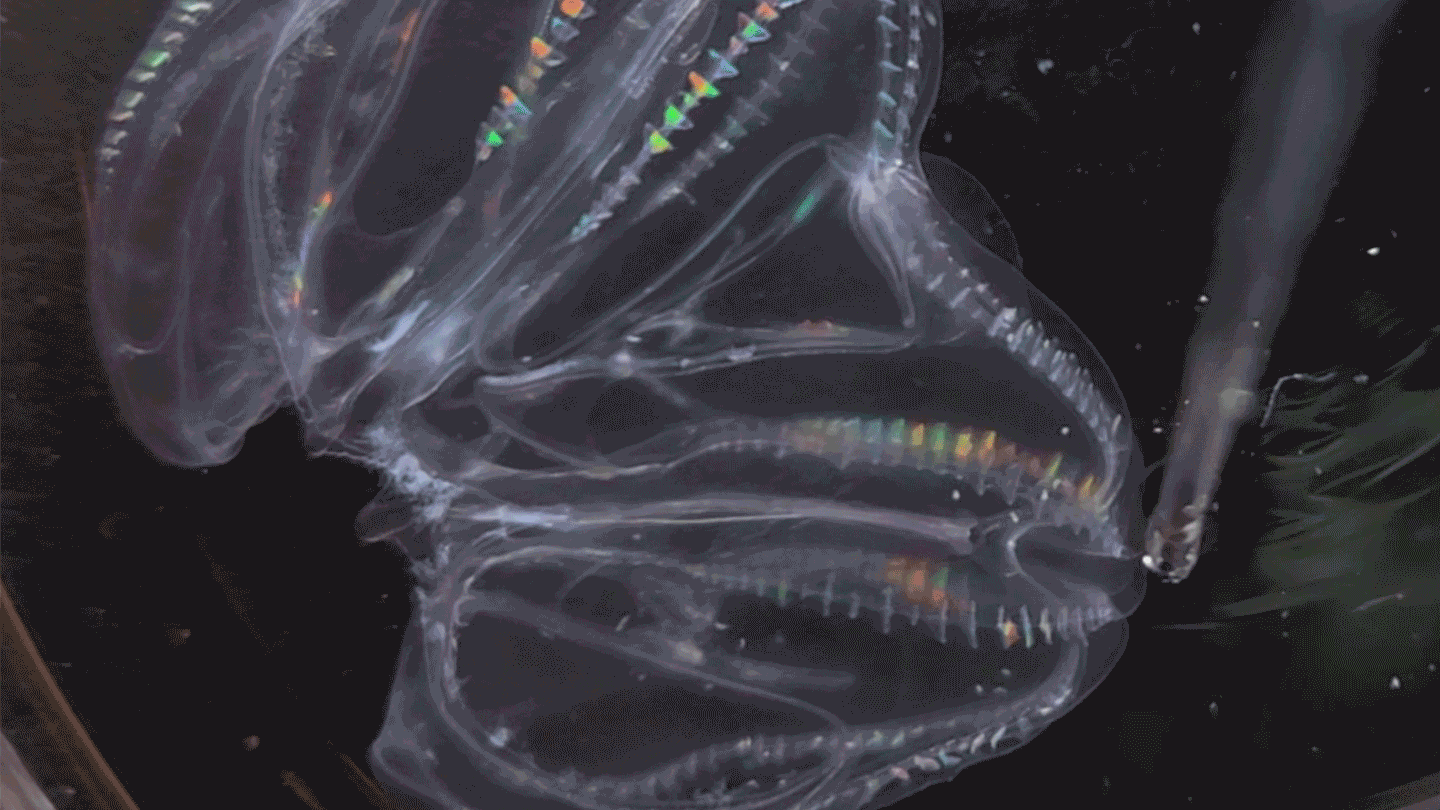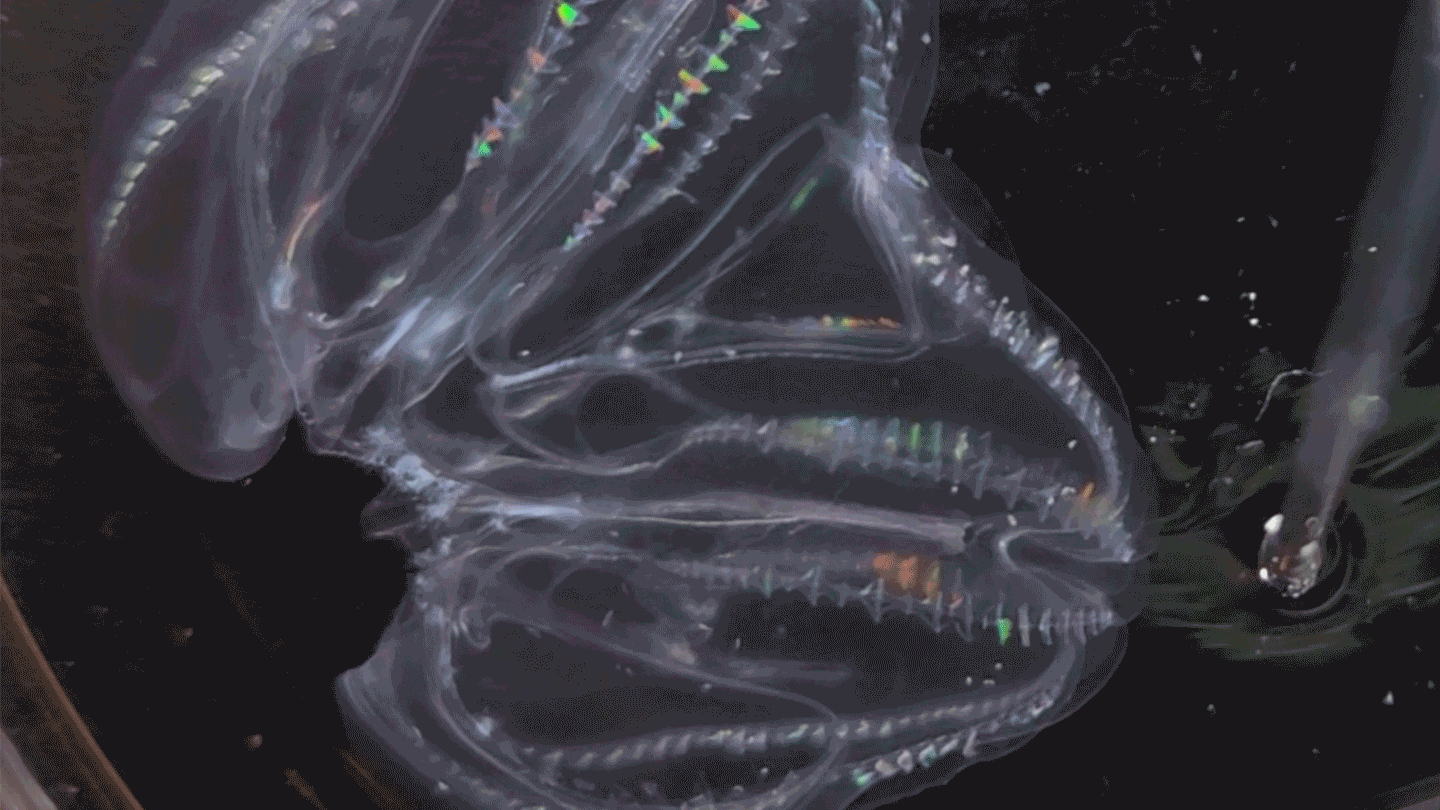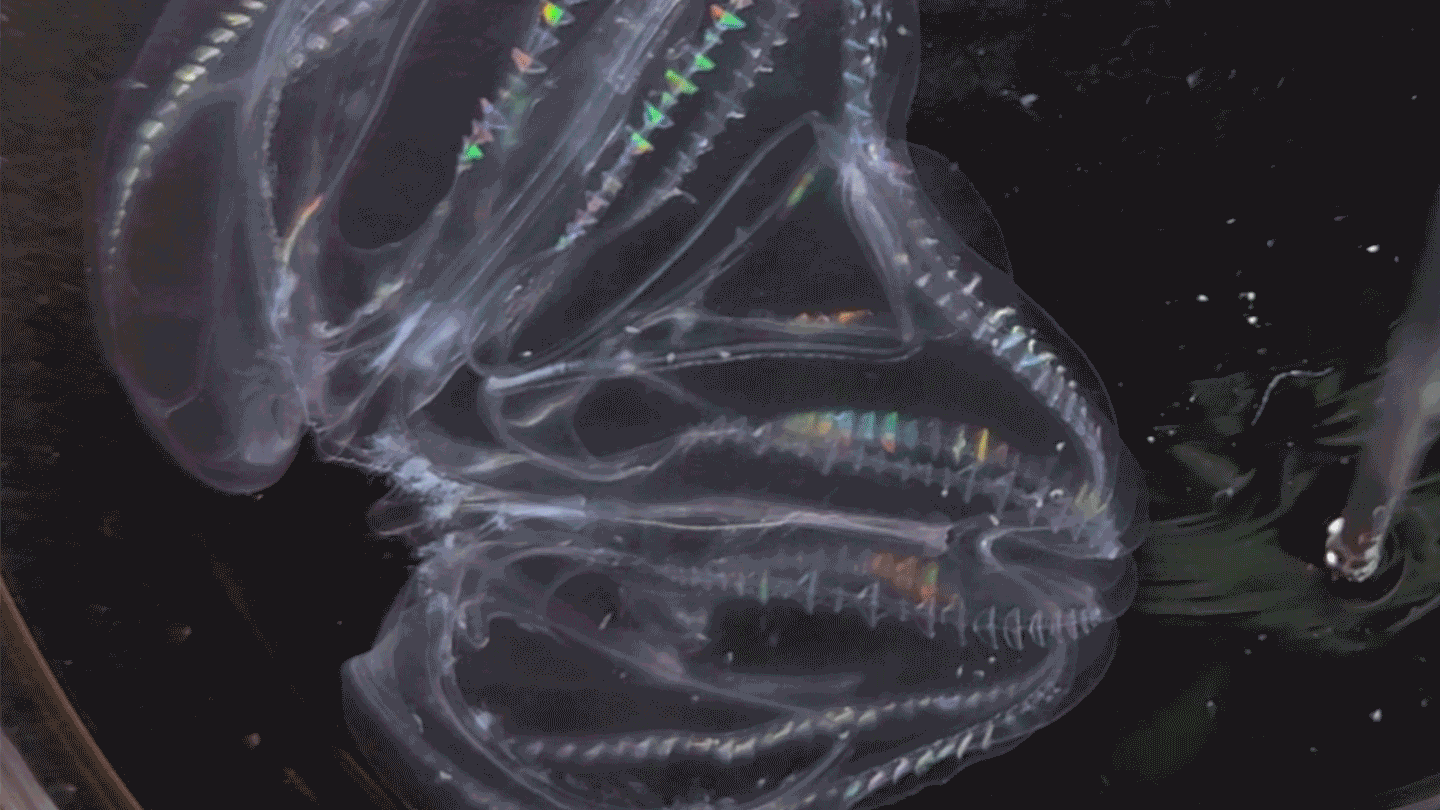
AnimalsThese sea creatures can fuse their bodies
A species of comb jelly can fuse its body with another jelly after injury. Some of the pair’s body functions then synchronize.
By Jude Coleman -
 Genetics
GeneticsThe discovery of microRNA wins the 2024 physiology Nobel Prize
Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun found a new principle of gene regulation essential for all multicellular organisms.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Sophie Hartley -

Embracing the collective nature of science
Editor in chief Nancy Shute celebrates this year's SN10: Scientists to Watch and novel approaches to research.
By Nancy Shute -

-
 Space
Space50 years ago, satellites threatened astronomers’ view of the cosmos
As satellite launches ramp up and the spacecraft clog the skies, astronomers fear for their data.
-
 Oceans
OceansA transatlantic flight may turn Saharan dust into a key ocean nutrient
Over time, atmospheric chemical reactions can make iron in dust from the Sahara easier for organisms to take in, helping to create biodiversity hot spots.
By Douglas Fox -
 Animals
AnimalsSome tadpoles don’t poop for weeks. That keeps their pools clean
Eiffinger’s tree frog babies store their solid waste in an intestinal pouch, releasing less ammonia into their watery cribs than other frog species.