Uncategorized
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnts practice combat triage and nurse their injured
Termite-hunting ants have their own version of combat medicine for injured nest mates.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomyJames Webb Space Telescope challenges artists to see in infrared
Astronomy artists face new challenges in translating James Webb’s invisible data into visuals.
-
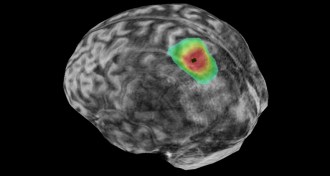 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTo hear the beat, your brain may think about moving to it
To keep time to a song, the brain relies on a region used to plan movement — even when you’re not tapping along.
By Dan Garisto -
 Animals
AnimalsStrong winds send migrating seal pups on lengthier trips
Prevailing winds can send northern fur seal pups on an epic journey.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHousehold products make surprisingly large contributions to air pollution
A study of smog in the Los Angeles valley finds that paints, fragrances and other everyday items are a growing component of the problem.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossil footprints may put lizards on two feet 110 million years ago
Fossilized footprints found in South Korea could be the earliest evidence of two-legged running in lizards.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyIn Borneo, hunting emerges as a key threat to endangered orangutans
Only small numbers of Bornean orangutans will survive coming decades, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Climate
ClimateLook to penguins to track Antarctic changes
Scientists say carbon and nitrogen isotopes found in penguin tissues can indicate shifts in the Antarctic environment.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsStudy debunks fishy tale of how rabbits were first tamed
A popular tale about rabbit domestication turns out to be fiction.
-
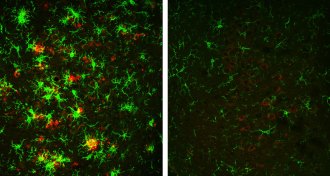 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCutting off a brain enzyme reversed Alzheimer’s plaques in mice
Inhibiting an enzyme involved in the production of Alzheimer’s protein globs also made old globs, or plaques, disappear in mouse brains.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum computers go silicon
Scientists performed the first quantum algorithms in silicon, and probed quantum bits with light.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenes could record forensic clues to time of death
Scientists have found predictable patterns in the way our genetic machinery winds down after death.