Uncategorized
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceReaders weigh in on human gene editing and more
Readers debated feeling morally obligated to edit their kid's genes and had questions about exoplanets.
-
 Health & Medicine
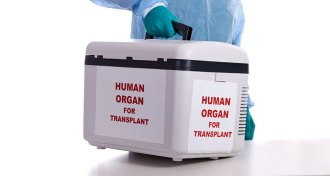
Health & Medicine50 years ago, early organ transplants brought triumph and tragedy
In 1968, the liver transplant field had its first small successes. Now, more than 30,000 patients in the U.S. receive a donated liver each year.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew fossils are redefining what makes a dinosaur
While some researchers question what characteristics define the dinosaurs, others are uprooting the dino family tree altogether.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyAn amateur astronomer caught a supernova explosion on camera
An amateur astronomer has caught a supernova explosion on camera.
-
 Life
LifeA fake organ mimics what happens in the blink of an eye
A newly crafted artificial eye could help researchers study treatments for dry eye disease and other ailments.
-
 Humans
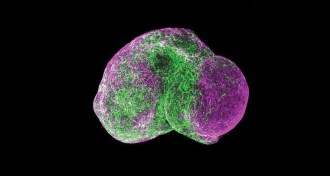
HumansHow to build a human brain
Organoids, made from human stem cells, are growing into brains and other miniorgans to help researchers study development
By Ingfei Chen -
 Plants
PlantsThe flowers that give us chocolate are ridiculously hard to pollinate
Cacao trees are really fussy about pollination.
By Susan Milius -
 Archaeology
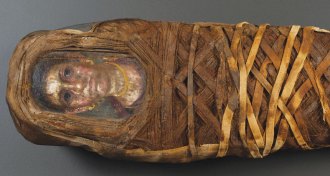
ArchaeologyModern tech unravels mysteries of Egyptian mummy portraits
A museum exhibit showcases what modern analytical tools can reveal about ancient Egyptian funerary portraits and mummies.
-
 Tech
TechMix of metals in this Picasso sculpture provides clues to its mysterious origins
The alloys used to cast Picasso’s bronze sculptures provide a valuable piece of the puzzle in reconstructing the histories of the works of art.
By Kate Travis -
 Neuroscience
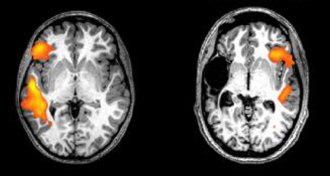
NeuroscienceBabies can recover language skills after a left-side stroke
Very young babies who have strokes in the language centers of their brain can recover normal language function — in the other side of their brain.
-
 Tech
TechThis stick-on patch could keep tabs on stroke patients at home
New wearable electronics that monitor swallowing and speech could aid rehabilitation therapy for stroke patients.
-
 Space
SpaceAmericans would welcome alien life rather than fear it
Americans would probably take the discovery of extraterrestrial microbes pretty well.