Uncategorized
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyArdi walked the walk 4.4 million years ago
Ancient hominid evolved upright stance without sacrificing climbing ability.
By Bruce Bower -
 Cosmology
CosmologyWhy the Nobel Prize might need a makeover
In Losing the Nobel Prize, astrophysicist Brian Keating discusses the downsides of science’s top honor.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow honeybees’ royal jelly might be baby glue, too
A last-minute pH shift thickens royal jelly enough to stick queen larvae to the ceiling of hive cells.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsThe truth about animals isn’t always pretty
The Truth About Animals digs up surprising stories about sloths, pandas, penguins and other wildly misunderstood wildlife.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe science behind cancer warnings on coffee is murky at best
The risks of acrylamide in coffee are not as clear as a California court ruling may suggest.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceEggshell nanostructure protects a chick and helps it hatch
The nanoscale structure of a chicken eggshell changes to fulfill different functions as the egg incubates.
-
 Animals
AnimalsToxins from the world’s longest animal can kill cockroaches
Bootlace worms can stretch up to 55 meters long and ooze toxins that can kill cockroaches and green crabs.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsSome frogs may be bouncing back after killer chytrid fungus
Frogs in Panama may be developing defenses against a fatal skin disease, a new study suggests.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeWhy cracking your knuckles can be so noisy
Knuckles crack due to the partial collapse of bubbles in joint fluid, a new study suggests.
-
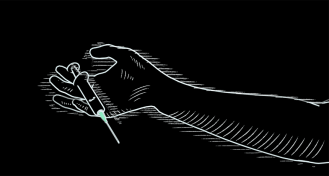 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOpioids kill. Here’s how an overdose shuts down your body
Powerful opioids affect many parts of the body, but the drugs’ most deadly effects are on breathing.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceLive heart cells make this material shift color like a chameleon
A new material made of heart cells from rats and hydrogel changes color as the living cells contract and relax.
-
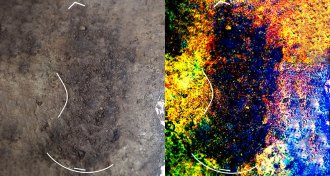 Archaeology
ArchaeologyFootprints put people on Canada’s west coast 13,000 years ago
Island tracks indicate early New World settlers traveled down the North American Pacific coast about 13,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower