Uncategorized
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsOne particle’s trek suggests that ‘spacetime foam’ doesn’t slow neutrinos
Neutrinos and light travel at essentially the same speed, as predicted.
-
 Health & Medicine
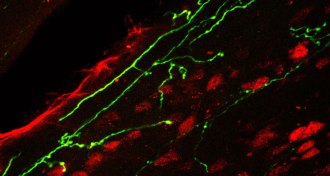
Health & MedicineHow a variation on Botox could be used to treat pain
Drugs that incorporate modified botulinum toxin provide long-term pain relief, a study in mice finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew ‘Poké Ball’ robot catches deep-sea critters without harming them
A machine that gently catches and releases animals underwater could help researchers take a more detailed census of the deep sea.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis amber nugget from Myanmar holds the first known baby snake fossil
Amber preserves the delicate bone structure of a 99 million year old baby snake.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMove over, Hubble. This sharp pic of Neptune was taken from Earth
A new strategy at the Very Large Telescope lets astronomers take space telescope–quality pictures from the ground.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAn ancient swimming revolution in the oceans may have never happened
Swimmers may not have suddenly dominated the oceans during the Devonian Period after all: New analyses suggest they took over much more gradually.
-
 Planetary Science
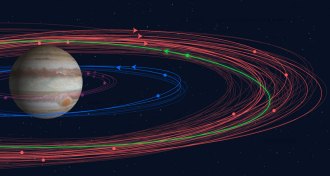
Planetary ScienceJupiter has 12 more moons than we knew about — and one is bizarre
Astronomers found a dozen previously unknown moons of Jupiter, and one may be a remnant of a larger moon that was all but ground to dust.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘The Poisoned City’ chronicles Flint’s water crisis
A new book examines how lead ended up in Flint’s water and resulted in a prolonged public health disaster.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentWildfires are making extreme air pollution even worse in the northwest U.S.
America’s air is getting cleaner — except in places that are prone to wildfires.
-
 Computing
ComputingSolving problems by computer just got a lot faster
A new computer program sifts through all possible solutions to find the best answer to a given problem far faster than other algorithms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe brain may clean out Alzheimer’s plaques during sleep
Sleep deprivation may speed up development of Alzheimer’s disease.
By Laura Beil -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceFirst global maps of Pluto and Charon show the worlds’ highs and lows
New charts of Pluto and its moon Charon, compiled using New Horizons’ data, reveal high peaks, deep depressions and strange ridges.