Uncategorized
-
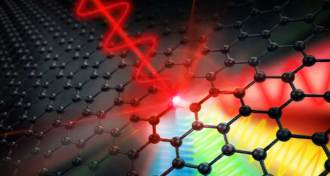 Materials Science
Materials ScienceHere’s how graphene could make future electronics superfast
Graphene-based electronics that operate at terahertz frequencies would be much speedier successors to today’s silicon-based devices.
-
 Physics
PhysicsSound waves can make bubbles in levitated drops of liquid
A new technique reveals how to make bubbles from droplets suspended in the air.
-
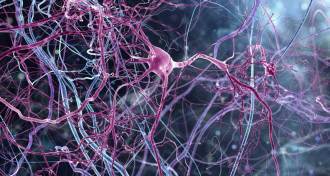 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow obesity may harm memory and learning
In obese mice, immune cells chomp nerve cell connections and harm brainpower.
-
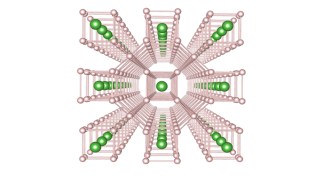 Physics
PhysicsA new hydrogen-rich compound may be a record-breaking superconductor
The record for the highest-temperature superconductor may be toast.
-
 Climate
ClimateWildfires make their own weather, and that matters for fire management
Mathematical equations describing interactions between wildfires and the air around them help explain their power and destruction.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyBefore it burned, Brazil’s National Museum gave much to science
When Brazil’s National Museum went up in flames, so did the hard work of the researchers who work there.
-
 Oceans
OceansA massive net is being deployed to pick up plastic in the Pacific
As the Ocean Cleanup project embarks, critics remain unconvinced that scooping up debris is the best way to solve the ocean’s plastic problem.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese songbirds violently fling and then impale their prey
A loggerhead shrike that skewers small animals on barbed wire gives mice whiplash shakeups.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomyJocelyn Bell Burnell wins big physics prize for 1967 pulsar discovery
Astrophysicist Jocelyn Bell Burnell speaks about winning the Breakthrough Prize, impostor syndrome and giving back.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureHow plant microbes could feed the world and save endangered species
Scientists have only scratched the surface of the plant microbiome, but they already believe it might increase crop yield and save species from extinction.
By Amber Dance -
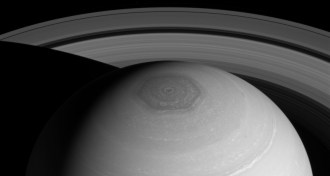 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSaturn has two hexagons, not one, swirling around its north pole
NASA’s Cassini spacecraft spied a vortex growing high over Saturn’s north pole, whose hexagonal shape mirrors a famous underlying cyclone.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, a pessimistic view for heart transplants
Surgeon Christiaan Barnard performed the first successful human-to-human heart transplant in 1967. In 1968, he predicted that patients would survive five years at best. Fortunately, he was wrong.