Uncategorized
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn a first, a woman with a uterus transplanted from a deceased donor gives birth
After receiving a uterus from a deceased donor, a woman gave birth to a healthy girl in December of 2017.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists’ collection of gravitational waves just got a lot bigger
The biggest black hole merger yet seen created one set of the spacetime ripples.
-
 Animals
AnimalsRebel honeybee workers lay eggs when their queen is away
A honeybee queen’s absence in the colony triggers some workers to turn queen-like and lay eggs, sometimes in other colonies.
By Yao-Hua Law -
 Life
LifeHow some sap-sucking insects fling their pee
Sharpshooters hurl their pee with structure called a stylus, which sends droplets flying at 20 times the acceleration of Earth’s gravity.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft has finally arrived at asteroid Bennu
Planetary scientists hope the probe will reveal if such carbon-rich asteroids helped kick-start life on Earth.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsThe Large Hadron Collider is shutting down for 2 years
The world’s largest particle accelerator will restart in 2021 at higher energy.
-
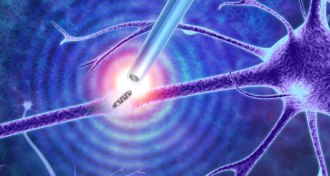 Life
LifeThese new tweezers let scientists do biopsies on living cells
Nanotweezers that can pluck molecules from cells without killing them could enable real-time analysis of the insides of healthy and diseased cells.
-
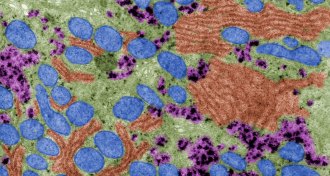 Life
LifeDads, not just moms, can pass along mitochondrial DNA
Data from three families suggest that in rare cases children can inherit mitochondria from their fathers.
-
 Climate
ClimateHalf the world’s annual rain falls in just 12 days
Climate change could shorten the time it takes for the world to receive half its annual precipitation from 12 days to 11 by 2100.
By Kyle Plantz -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyStone Age people conquered the Tibetan Plateau’s thin air
Stone tools that are at least 30,000 years old suggest that people settled the high-altitude Tibetan Plateau earlier than scientists thought.
By Bruce Bower -
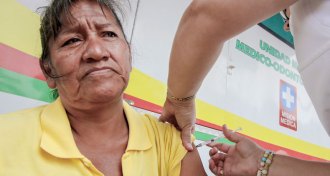 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAround the world, reported measles cases jumped 31 percent in 2017
While the number of reported measles cases has dropped 80 percent from 2000 to 2017, high profile outbreaks pushed the 2017 total up from 2016.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentAn acid found in soil may make a disease killing deer less infectious
An incurable neurodegenerative disease crippling North American deer, elk and moose may be thwarted by an organic soil compound.