Uncategorized
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenes might explain why dogs can’t sniff out some people under stress
Genes and stress may change a person’s body odor, confusing police dogs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTreating mosquitoes may be a new way to fight malaria
A lab test suggests it may be possible to treat mosquitoes infected with the malaria parasite to stop disease transmission.
-
 Astronomy
Astronomy3 explanations for ‘Oumuamua that aren’t alien spaceships
Astronomers are coming up with some creative ideas to explain the weird behavior of the first known interstellar object.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExtreme elements push the boundaries of the periodic table
The hunt for the next elements on the periodic table might turn up superheavy atoms that flaunt the rules of chemistry.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA long handshake can spread your DNA to objects you didn’t touch
Two new studies show that even brief contact with another person or object could transfer your DNA far and wide.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWith its burning grip, shingles can do lasting damage
Varicella zoster virus, which causes chickenpox and shingles, may instigate several other problems.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyScientists set sail for the elusive island of stability
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses the search for the island of stability and the future of the periodic table.
By Nancy Shute -
 Animals
Animals‘Mama’s Last Hug’ showcases the emotional lives of animals
In ‘Mama’s Last Hug,’ Frans de Waal argues that emotions occur throughout the animal world.
By Erin Wayman -
 Life
LifeReaders ponder mitochondria, Neandertal diets, deep sea corals and more
Readers had questions about mitochondrial DNA, Neandertal diets, deep ocean corals and more.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient Angkor’s mysterious decline may have been slow, not sudden
Analyzing sediment from the massive city’s moat challenges the idea that the last capital of the Khmer Empire collapsed suddenly.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsHermit crabs are drawn to the smell of their own dead
A new study finds that the smell of hermit crab flesh attracts other hermit crabs of the same species desperately looking for a larger shell.
By Yao-Hua Law -
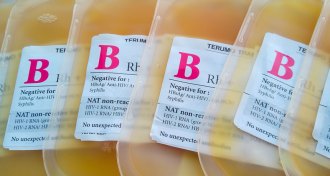 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe FDA says don’t buy young plasma therapies. Here’s why
Infusions of plasma from young people may hold the secret of youth, but there’s not much evidence to support the idea yet.