Uncategorized
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyYou’re only as old as you perceive yourself to be
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses how people’s attitudes about aging can impact our physical health.
By Nancy Shute -
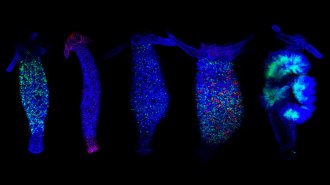 Life
LifeMapping how the ‘immortal’ hydra regrows cells may demystify regeneration
In the continually regenerating hydra, fluorescent markers help researchers track stem cells on the way to their cellular fate.
-
 Life
LifeGiving cats food with an antibody may help people with cat allergies
Research by pet-food maker Purina aims to disable the major allergen carried in cat saliva, a protein called Fel d1.
-
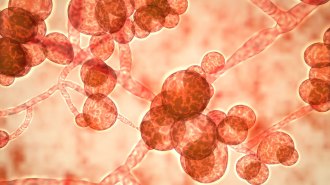 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClimate change could raise the risk of deadly fungal infections in humans
The rise of Candida auris, a deadly fungus spurring outbreaks in the United States and worldwide, may have been aided by climate change.
-
 Life
LifeImmune system defects seem to contribute to obesity in mice
Subtle defects affecting T cells altered the animals’ microbiome and fat absorption, providing hints of what might also be going on in people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, a drug that crippled a generation found new life as a leprosy treatment
In 1969, a drug that crippled a generation found new life as a treatment for leprosy.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyNASA’s Chandra X-ray telescope celebrates 20 years in space
The U.S. space agency has released new images for the Chandra X-ray Observatory’s 20th birthday.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsDark matter particles won’t kill you. If they could, they would have already
The fact that no one has been killed by shots of dark matter suggests the mysterious substance is relatively small and light.
-
 Climate
ClimateHow today’s global warming is unlike the last 2,000 years of climate shifts
Temperatures at the end of the 20th century were hotter almost everywhere on the planet than in the previous two millennia.
-
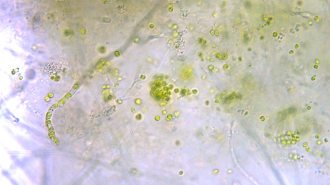 Life
LifeThis is the first fungus known to host complex algae inside its cells
In the lab, an alga and a fungus teamed up to exchange food, similar to lichens. But instead of staying outside, the alga moved into the fungal cells.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA frog study may point to where parenting begins in the brain
Two brain regions, including one active in mammal parents, lit up with activity in both male and female poison frogs when caring for their tadpoles.
-
 Archaeology
Archaeology‘Fruit from the Sands’ explores the Silk Road origins of apples, tea and more
A new book explains how many of today’s popular foods got started on Central Asia’s ancient Silk Road trade networks.
By Bruce Bower