Uncategorized
-
 Animals
AnimalsTiny structures in dragonfish teeth turn them into invisible daggers
The teeth of deep-sea dragonfish are transparent because of nanoscale crystals and rods that let light pass through without being scattered.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentChemicals in biodegradable food containers can leach into compost
PFAS compounds from compostable food containers could end being absorbed by plants and later eaten by people, though the health effects are unclear.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThe Smithsonian’s ‘Deep Time’ exhibit gives dinosaurs new life
The Smithsonian’s renovated fossil hall puts ancient dinosaurs and other creatures in context.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentHow one fern hoards toxic arsenic in its fronds and doesn’t die
To survive high levels of arsenic, a fern sequesters the heavy metal in its shoots with the help of three proteins.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA new experiment didn’t find signs of dreaming in brain waves
Brain activity that powers dreams may reveal crucial insight into consciousness, but a new study failed to spot evidence of the neural flickers.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHominids may have been cutting-edge tool makers 2.6 million years ago
Contested finds point to a sharp shift in toolmaking by early members of the Homo genus.
By Bruce Bower -
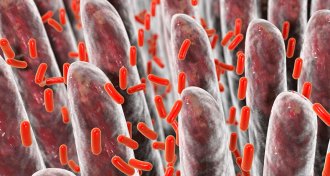 Life
LifeGut bacteria may change the way many drugs work in the body
A new survey of interactions between microbes and medications suggests that gut bacteria play a crucial role in how the body processes drugs.
-
 Physics
PhysicsThis tabletop device turns the quantum definition of a kilogram into a real mass
The mini Kibble balance will measure 10 grams to an accuracy of a few ten-thousandths of a percent.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe Southern Ocean may be less of a carbon sink than we thought
The Southern Ocean’s ability to suck up much of the carbon that humans pump into the atmosphere is in question.
-
 Climate
ClimateThousands of birds perished in the Bering Sea. Arctic warming may be to blame
A mass die-off of puffins and other seabirds in the Bering Sea is probably linked to climate change, scientists say.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyCave debris may be the oldest known example of people eating starch
Charred material found in South Africa puts energy-rich roots and tubers on Stone Age menus, long before farming began.
By Bruce Bower -
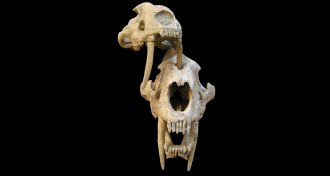 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossils reveal saber-toothed cats may have pierced rivals’ skulls
Two Smilodon fossil skulls from Argentina have puncture holes likely left by the teeth of rival cats.