Uncategorized
-
 Physics
PhysicsMonika Schleier-Smith leads elaborate quantum conversations
Monika Schleier-Smith forces atoms to interact in ways that could offer insights into quantum computing, precision timekeeping and perhaps black holes.
-

Readers question killer macros and spinning wheels
Readers had questions about theoretical dark matter particles and textile archaeology.
-

Scientists who aren’t afraid to range across disciplines
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses 10 early- and mid-career scientists who are making cross-disciplinary connections.
By Nancy Shute -
 Genetics
GeneticsDog behaviors like aggression and fearfulness are linked to breed genetics
A study looking at how 101 dog breeds behave finds a strong association between genetics and 14 personality traits.
-
 Health & Medicine
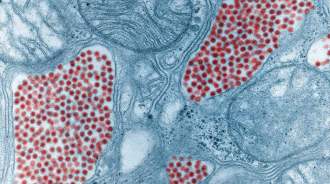
Health & MedicineRare eastern equine encephalitis has killed 9 people in the U.S. in 2019
2019 is the worst eastern equine encephalitis outbreak since tracking began in 2003, with 31 cases and nine deaths from the brain infection so far.
By Sofie Bates -
 Humans
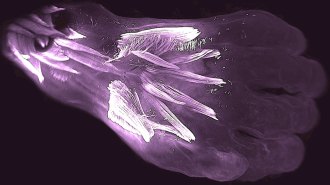
HumansHuman embryos have extra hand muscles found in lizards but not most adults
In developing human embryos, muscles are made, then lost, in a pattern that mirrors the appearance of the structures during evolution.
-
 Earth
EarthHere’s where Earth stores its carbon
Most of Earth’s carbon is stored inside the planet. But giant lava outflows and now humans have released huge amounts of carbon into the atmosphere.
-
 Earth
EarthHurricane Lorenzo hit Category 5 farther east than any other storm
Lorenzo reached category 5 status on September 28, making it the northern-most and eastern-most category 5 hurricane ever recorded in the Atlantic.
By Sofie Bates -
 Humans
HumansPersonalized diets may be the future of nutrition. But the science isn’t all there yet
How a person responds to food depends on more than the food itself. But what exactly is still a confusing mix of genes, microbes and other factors.
-
 Space
Space‘Imagined Life’ envisions the odd critters of other planets
The authors of ‘Imagined Life’ rely on science to sketch out what kind of organisms might exist on exoplanets.
By Sid Perkins -
 Space
SpaceNASA’s new black hole visualizations showcase how gravity warps light
Images from computer simulations highlight how the extreme gravity of a black hole tampers with light rays emanating from its accretion disk to create weird patterns.
-
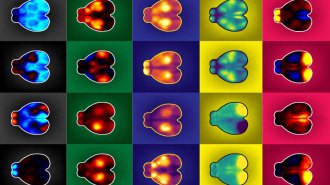
Mice fidget. Those motions have big effects on their brains
Unnecessary motion has a profound and widespread effect on nerve cell behavior in mice.