Uncategorized
-
 Space
SpaceA planetary body may have smashed into Jupiter, creating its weird core
A planetary body smashing into Jupiter may have jostled the gas giant’s insides during its formative years, creating the strange interior seen today.
-
 Life
LifeCRISPR enters its first human clinical trials
The gene editor will be used in lab dishes in cancer and blood disorder trials, and to directly edit a gene in human eyes in a blindness therapy test.
-
 Humans
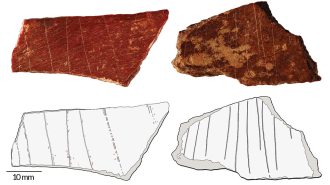
HumansEngraved bones reveal that symbolism had ancient roots in East Asia
Denisovans might have etched line patterns on two animal bone fragments more than 100,000 years ago in what’s now northern China.
By Bruce Bower -
 Space
SpaceAstronomers just quintupled the number of known repeating fast radio bursts
A Canadian telescope spotted eight more repeating fast radio bursts. What causes these cryptic flashes of radio waves from deep space remains unclear.
-
 Life
LifeA mussel poop diet could fuel invasive carp’s spread across Lake Michigan
Asian carp, just a human-made waterway away from reaching Lake Michigan, could live in much more of the lake than previously thought.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTwo of four Ebola treatments prove highly effective in a clinical trial
An Ebola field trial is shifting its focus toward two treatments that have been shown to be highly effective at preventing death in Congo, according to preliminary data.
-
 Humans
HumansEven without concussions, just one football season may damage players’ brains
A group of college football players underwent brain scans after a season of play. The results suggest the sport could impact neural signaling.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePlants don’t have feelings and aren’t conscious, a biologist argues
The rise of the field of “plant neurobiology” has this scientist and his colleagues pushing back.
-
 Space
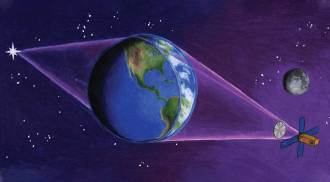
SpaceA proposed space telescope would use Earth’s atmosphere as a lens
One astronomer has a bold solution to the high cost of building big telescopes.
-
 Humans
HumansAre researchers asking the right questions to prevent mass shootings?
Understanding how to thwart these violent events may be more effective than analyzing perpetrators’ backgrounds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Physics
PhysicsExploding stars scattered traces of iron over Antarctic snow
Researchers melted half a ton of snow to find just 10 atoms of a radioactive variety of iron.
-
 Life
LifeHow these tiny insect larvae leap without legs
High-speed filming reveals how a blob of an insect can leap more efficiently than it crawls.
By Susan Milius