Uncategorized
-
 Earth
EarthImproved three-week weather forecasts could save lives from disaster
Meteorologists are pushing to make forecasts good enough to fill the gap between short-term and seasonal.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyMandatory mail-in voting hurts neither Democratic nor Republican candidates
A new study suggests that requiring people to cast mail-in ballots actually leads to a slightly increased turnout for both political parties.
By Sujata Gupta -
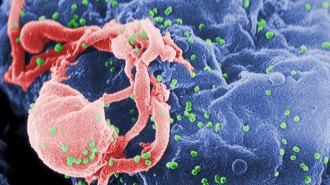 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIn a first, a person’s immune system fought HIV — and won
Some rare people may purge most HIV from their bodies, leaving only broken copies of the virus or copies locked in molecular prisons, from which there is no escape.
-
 Earth
EarthCarbon dioxide from Earth’s mantle may trigger some Italian earthquakes
In the central Apennines of Italy, spikes in natural carbon dioxide emissions line up with the biggest earthquakes.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesIf bacteria band together, they can survive for years in space
Tiny clumps of bacteria can survive at least three years in outer space, raising the prospect of interplanetary travel by microbial life.
-
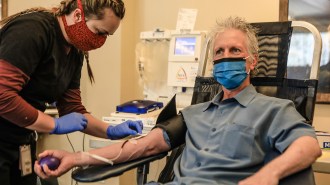 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19 plasma treatments may be safe, but we don’t know if they work
Blood plasma from COVID-19 survivors can be used to treat hospitalized patients, FDA says, but researchers question how well it works.
By Jonathan Lambert and Tina Hesman Saey -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat we can learn from how a doctor’s race can affect Black newborns’ survival
When Black physicians attended Black newborns after a hospital birth, it reduced the mortality gap between Black and white babies.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFemale hyenas kill off cubs in their own clans
Along with starvation and mauling by lions, infanticide leads as a cause of hyena cub death. Such killings may serve to enforce the social order.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA man in Hong Kong is the first confirmed case of coronavirus reinfection
During a 33-year-old man’s first round with the virus, he had symptoms, but not the second time — a hint his immune system protected him from disease.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsA measurement of positronium’s energy levels confounds scientists
A gap in the energy levels of positronium seems to be substantially larger than predicted, and physicists don’t know why.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew treatments aim to treat COVID-19 early, before it gets serious
Some new drugs that may stop the coronavirus from getting into cells, or from reproducing itself, may treat the illness as soon as it’s diagnosed.
-
