Uncategorized
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s what we’ve learned in six months of COVID-19 — and what we still don’t know
Six months into the new coronavirus pandemic, researchers have raced to uncover crucial information about SARS-CoV-2. But much is still unknown.
-
 Life
LifeHere’s how flying snakes stay aloft
High-speed cameras show that paradise tree snakes keep from tumbling as they glide through the sky by undulating their bodies.
-
 Life
LifeFish eggs can hatch after being eaten and pooped out by ducks
In the lab, a few carp eggs survived and even hatched after being pooped out by ducks. The finding may help explain how fish reach isolated waterways.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyMonkeys may share a key grammar-related skill with humans
A contested study suggests the ability to embed sequences within other sequences, a skill called recursion and crucial to grammar, has ancient roots.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy scientists say wearing masks shouldn’t be controversial
New data suggest that cloth masks work to reduce coronavirus cases, though less well than medical masks.
-

50 years ago, scientists first investigated antibiotic resistance in livestock
In 1970, scientists began investigating the effects of feeding antibiotics to livestock. 50 years later, we know it can be harmful for humans.
-
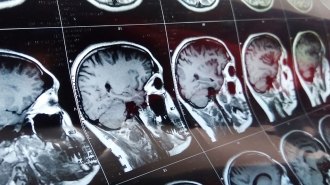 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStrokes and mental state changes hint at how COVID-19 harms the brain
In a group of people severely ill from the coronavirus, strokes, psychosis, depression and other brain-related changes come as complications.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe second-worst Ebola outbreak ever is officially over
As Congo grapples with COVID-19 and other disease outbreaks, the country’s 10th battle against Ebola has ended.
-
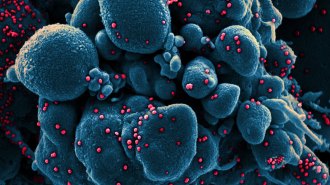 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMillions of COVID-19 cases in the U.S. may have gone undiagnosed in March
Millions of people in the United States went to the doctor in March with influenza-like symptoms. Many may have had COVID-19, a study suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDolphins can learn from peers how to use shells as tools
While most foraging skills are picked up from mom, some bottlenose dolphins seem to look to their peers to learn how to trap prey in shells.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Earth
EarthTwo lightning megaflashes shattered distance and duration records
Satellite data show that the two extreme bolts, both appearing over South America, more than doubled the previous records.
-
 Space
SpaceColliding black holes may have created a surprising flare of light
A flare-up after a gravitational wave outburst may be the first sighting of light from colliding black holes.