Uncategorized
-
 Space
SpaceA ‘lake’ on Mars may be surrounded by more pools of water
Radar data hint at patches of liquid water beneath Martian polar ice, but some urge caution in interpreting results.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘Schrödinger’s Web’ offers a sneak peek at the quantum internet
For an entertaining overview of the physics and technological advances paving the way for the quantum internet, read ‘Schrödinger’s Web.’
By Dan Garisto -
 Physics
PhysicsA stop-motion experiment reveals supercooled water’s dual nature
Scientists found signs that water cooled well below freezing consists of two different arrangements of molecules.
-
 Health & Medicine
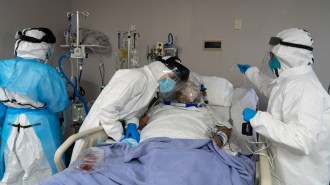
Health & MedicineDefects in early immune responses underlie some severe COVID-19 cases
Scientists are finding that strong early immune responses to the coronavirus are crucial to protect some people from developing life-threatening symptoms.
-
 Space
SpaceA new moon radiation measurement may help determine health risks to astronauts
China's lunar lander measured radiation at the moon’s surface, finding the daily dose is 2.6 times as high as inside the International Space Station.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsTrapped under ice, light-loving algae grow in the dark Arctic winter
Blocked off from nearly all light beneath a thick layer of ice and snow in the winter, marine phytoplankton in the Arctic still find a way to thrive.
-
 Neuroscience
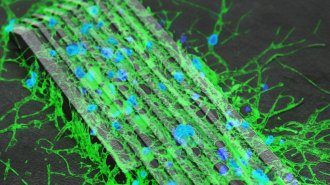
NeuroscienceTiny, magnetically controlled robots coax nerve cells to grow connections
Research using microrobots and nerve cells from rats could point to new treatments for people with nerve injuries.
-
 Space
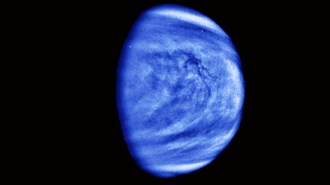
SpaceHope for life on Venus survives for centuries against all odds
Early scientists often assumed that Venus, though hotter than Earth, hosted life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA Brazilian city devastated by COVID-19 may have reached herd immunity
Up to half of Manaus was infected at the epidemic’s peak, which slowed further spread of the virus but also led to many deaths, scientists say.
-
 Life
LifeLife on Earth may have begun in hostile hot springs
What researchers learn at hot springs and seafloor vents may guide the search for life on icy moons and Mars.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Animals
AnimalsA beaked whale’s nearly four-hour-long dive sets a new record
The animals may rely on large stores of oxygen, a slow metabolism and the ability to tolerate lactic acid to go for hours without surfacing for air.
-
 Climate
ClimateGlobal warming may lead to practically irreversible Antarctic melting
Simulations suggest that even if the Paris climate goals are met, melting Antarctica ice will still cause sea levels to rise by more than 2 meters.