Uncategorized
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThe gap in parenting time between middle- and working-class moms has shrunk
Some well-educated mothers are spending less time with their kids than before, while some less-educated mothers are spending more, a new study shows.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Environment
EnvironmentWhy planting tons of trees isn’t enough to solve climate change
Massive projects need much more planning and follow-through to succeed – and other tree protections need to happen too.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceThese weird, thin ice crystals are springy and bendy
Specially grown fibers of frozen water bend into curves and spring back when released.
-
 Life
LifeSea otters stay warm thanks to leaky mitochondria in their muscles
For the smallest mammal in the ocean, staying warm is a challenge. Now, scientists have figured out how the animals keep themselves toasty.
-
 Plants
PlantsHow Romanesco cauliflower forms its spiraling fractals
By tweaking just three genes in a common lab plant, scientists have discovered the mechanism responsible for one of nature’s most impressive fractals.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow your DNA may affect whether you get COVID-19 or become gravely ill
A study of 45,000 people links 13 genetic variants to higher COVID-19 risks, including a link between blood type and infection and a newfound tie between FOXP4 and severe disease.
-
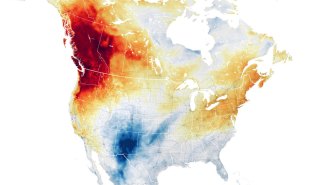 Climate
ClimateHuman-driven climate change sent Pacific Northwest temperatures soaring
As scientists dissect what pushed temperatures up to 5 degrees Celsius above previous records, they may have to revamp how to predict heat waves.
-
 Space
SpaceSouped-up supernovas may produce much of the universe’s heavy elements
An old star that formed from an explosive event called a magnetorotational hypernova is revealing where elements like uranium and silver might be forged.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureA tweaked yeast can make ethanol from cornstalks and a harvest’s other leftovers
By genetically modifying baker’s yeast, scientists figured out how to get almost as much ethanol from cornstalks as kernels.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow antibodies may cause rare blood clots after some COVID-19 vaccines
Vaccine-induced antibodies attach to a specific spot on a protein involved in clot formation, a study suggests.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA shadowy birthplace may explain Jupiter’s strange chemistry
Dust that blocked sunlight caused the giant planet to form in a deep freeze, a new study suggests.
By Ken Croswell -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow Hans Berger’s quest for telepathy spurred modern brain science
In the 1920s, psychiatrist Hans Berger invented EEG and discovered brain waves — though not long-range signals.