Uncategorized
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew studies hint that the coronavirus may be evolving to become more airborne
More coronavirus RNA is in fine aerosols than in larger droplets, but masks can reduce the amount of virus in the air.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSunbirds’ dazzling feathers are hot, in both senses of the word
Iridescent feathers reflect vivid colors. But they also become scorching hot in the sunlight, a study finds.
By Jake Buehler -
 Space
SpaceVera Rubin’s work on dark matter led to a paradigm shift in cosmology
‘Bright Galaxies, Dark Matter, and Beyond’ tells the story of how astronomer Vera Rubin provided key evidence for the existence of dark matter.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyA 1,000-year-old grave may have held a powerful nonbinary person
A medieval grave in Finland, once thought to maybe hold a respected woman warrior, may belong to someone who didn’t have a strictly male or female identity.
By Bruce Bower -
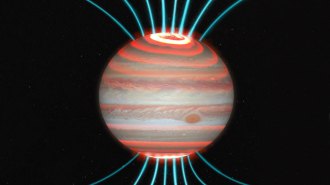 Space
SpaceJupiter’s intense auroras superheat its upper atmosphere
Jupiter’s hotter-than-expected upper atmosphere may be caused by high-speed charged particles slamming into the air high above the poles.
By Sid Perkins -
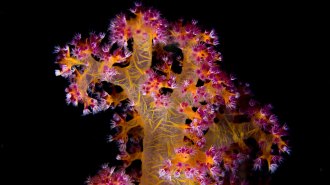 Life
LifeProbiotics help lab corals survive deadly heat stress
In a lab experiment, probiotics prevented the death of corals under heat stress, suggesting beneficial microbes could help save ailing reefs.
-
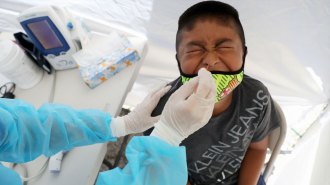 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow different COVID-19 testing plans can help keep kids safe in school
As children head back to school in the United States, here’s a look at various testing strategies that could keep kids safe during in-person learning.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMeasuring a black hole’s mass isn’t easy. A new technique could change that
The timing of flickers in the gas and dust in a black hole’s accretion disk correlates to its mass, a new study finds.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyHow the strange idea of ‘statistical significance’ was born
A mathematical ritual known as null hypothesis significance testing has led researchers astray since the 1950s.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsAn Indigenous people in the Philippines have the most Denisovan DNA
Genetic comparisons crown the Indigenous Ayta Magbukon people as having the most DNA, 5 percent, from the mysterious ancient hominids.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeScientists have a new word for birds stealing animal hair
Dozens of YouTube videos show birds stealing hair from dogs, cats, humans, raccoons and even a porcupine — a behavior rarely documented by scientists.
-
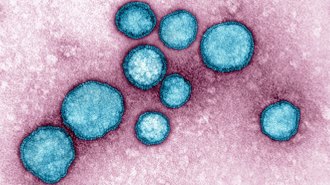 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineColds and other common respiratory diseases might surge as kids return to school
Recent historically low levels of some respiratory illnesses may lead to outbreaks this fall and winter, creating disruptions as kids return to school.