Uncategorized
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA bird with a T. rex head may help reveal how dinosaurs became birds
The 120-million-year-old Cratonavis zhui, newly discovered in China, had a head like a theropod and body like a modern bird.
-
 Animals
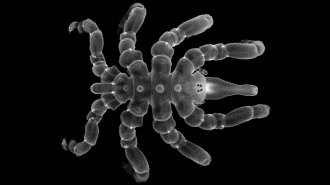
AnimalsSome young sea spiders can regrow their rear ends
Juvenile sea spiders can regenerate nearly all of their bottom halves — including muscles and the anus — or make do without them.
-
 Earth
EarthEarth’s inner core may be reversing its rotation
In the past 13 years, the rotation of the planet’s solid inner core may have temporarily stopped and then started to reverse direction.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Animals
AnimalsA rare rabbit plays an important ecological role by spreading seeds
Rabbits aren’t thought of as seed dispersers, but the Amami rabbit of Japan has now been recorded munching on a plant’s seeds and pooping them out.
-

-

Yes, we can meet the climate change challenge
Editor in chief Nancy Shute discusses the first installment of our new climate change solutions series.
By Nancy Shute -
 Environment
EnvironmentRecycling rare earth elements is hard. Science is trying to make it easier
As demand grows, scientists are inventing new — and greener — ways to recycle rare earth elements.
By Erin Wayman -
 Environment
EnvironmentRare earth elements could be pulled from coal waste
The scheme would provide valuable rare earth metals and help clean up coal mining’s dirty legacy.
By Erin Wayman -
 Astronomy
AstronomyNew data show how quickly light pollution is obscuring the night sky
Tens of thousands of observations from citizen scientists spanning a decade show that the night sky is getting about 10 percent brighter every year.
-
 Animals
AnimalsChicken DNA is replacing the genetics of their ancestral jungle fowl
Up to half of modern jungle fowl genes have been inherited from domesticated chickens. That could threaten the wild birds’ long-term survival.
By Jake Buehler -
 Health & Medicine
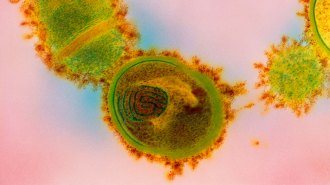
Health & MedicineToo much of this bacteria in the nose may worsen allergy symptoms
Hay fever sufferers have an overabundance of Streptococcus salivarius. The mucus-loving bacteria boost inflammation, causing an endlessly runny nose.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceWant a ‘Shrinky Dinks’ approach to nano-sized devices? Try hydrogels
Patterning hydrogels with a laser and then shrinking them down with chemicals offers a way to make nanoscopic structures out of many materials.