Uncategorized
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe FDA has approved the first-ever vaccine for RSV
GSK’s shot, for those 60 and over, can protect against severe respiratory syncytial virus. Other vaccines, including to protect newborns, are in the works.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyFor the first time, astrophysicists have caught a star eating a planet
A burst of light and a cloud of dust are signs that a star 12,000 light-years away swallowed a planet up to 10 times the mass of Jupiter.
-
 Archaeology
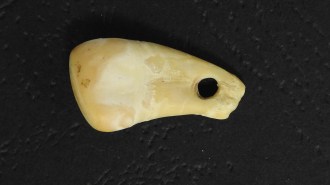
ArchaeologyAncient human DNA was extracted from a 20,000-year-old deer tooth pendant
Insights into Stone Age people’s lives may soon come from a new, nondestructive DNA extraction method.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsA 2,200-year-old poop time capsule reveals secrets of the Andean condor
Guano that has accumulated in a cliffside Andean condor nest for 2,200 years reveals how the now-vulnerable birds responded to a changing environment.
By Jake Buehler -
 Health & Medicine
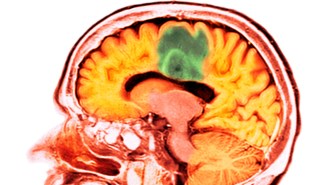
Health & MedicineUltrasound allows a chemotherapy drug to enter the human brain
An early-stage clinical trial demonstrates a technique for getting a powerful chemotherapy drug past the usually impenetrable blood-brain barrier.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis marine biologist is on a mission to save endangered rays
Jessica Pate and the Florida Manta Project confirm that endangered mantas are mating and sicklefin devils are migrating along the East Coast.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNeuroscientists decoded people’s thoughts using brain scans
The finding may lead to better communication aids for people who can’t communicate easily. It also raises privacy concerns.
-
 Health & Medicine
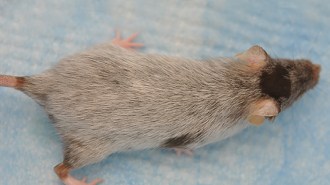
Health & MedicineMouse hair turns gray when certain stem cells get stuck
Stem cells involved in giving hair its color must keep moving and changing maturity levels to prevent graying, a mouse study suggests.
-

The animal kingdom never ceases to amaze
Editor in chief Nancy Shute revels in the wonder of animals, from psychedelic toads to extinct pterosaurs.
By Nancy Shute -
 Oceans
OceansSatellite data reveal nearly 20,000 previously unknown deep-sea mountains
By looking for tiny bumps in sea level caused by the gravity of subsurface mountains, researchers have roughly doubled the number of known seamounts.
-

-
 Physics
PhysicsBlack holes resolve paradoxes by destroying quantum states
A classic quantum experiment done near a black hole would create a paradox, physicists report. But not if the black hole collapses quantum states.