Uncategorized
-
 Physics
Physics50 years ago, superconductors were warming up
Superconducting temperatures have risen by about 250 degrees since the 1970s, but are still too cold to enable practical technologies.
-

How patient-led research is advancing science
Editor in chief Nancy Shute considers the role that people suffering from a variety of chronic conditions are starting to play in medical research.
By Nancy Shute -

-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLong COVID brain fog may be due to damaged blood vessels in the brain
MRI scans of long COVID patients with brain fog suggest that the blood brain barrier may be leaky.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsDaddy longlegs look like they have two eyes. That doesn’t count the hidden ones
Despite its two-eyed appearance, Phalangium opilio has six peepers. The four optical remnants shed light on the arachnids’ evolutionary history.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceTitan’s dark dunes could be made from comets
Saturn’s largest moon could have gotten its sands from an ancient reshuffling of the solar system. If true, that would solve a long-standing mystery.
By Nikk Ogasa -
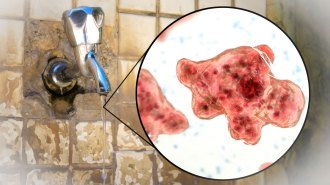 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDon’t use unsterilized tap water to rinse your sinuses. It may carry brain-eating amoebas
Two new studies document rare cases in which people who rinsed sinuses with unsterilized tap got infected with brain-eating amoebas.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMale dragonflies’ wax coats might protect them against a warming climate
The reflective wax, which cools males on sunny courtship flights, may also armor them against the effects of climate change.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsMale mammals aren’t always bigger than females
In a study of over 400 mammal species, less than half have males that are, on average, heavier than females, undermining a long-standing assumption.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe U.S. now has a drug for severe frostbite. How does it work?
Iloprost has been shown to prevent the need to amputate frozen fingers and toes. It’s now approved for use to treat severe frostbite in the U.S.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA decades-old mystery has been solved with the help of newfound bee species
Masked bees in Australia and French Polynesia have long-lost relatives in Fiji, suggesting that the bees’ ancestors island hopped.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFour years on, the COVID-19 pandemic has a long tail of grief
Researchers are studying the magnitude and impact that grief from the COVID-19 pandemic has had and will have for years to come.