50 years ago, artificial limbs weren’t nearly as responsive
Excerpt from the November 18, 1967 issue of Science News
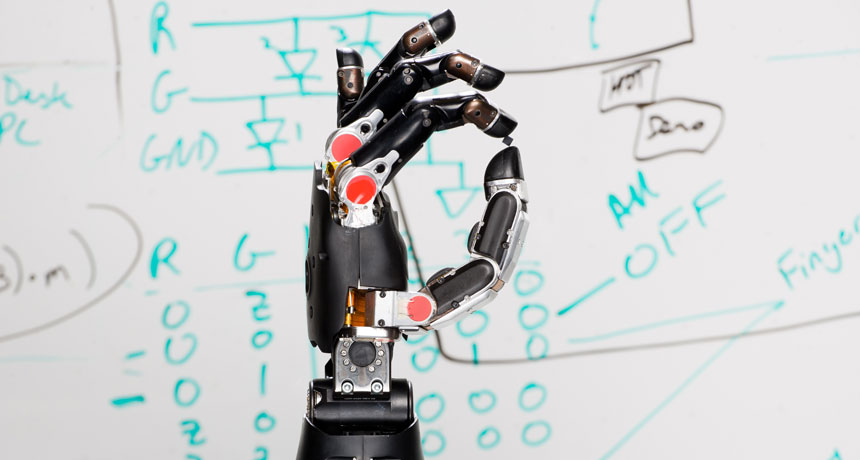
LIFE AND LIMB Prostheses have come a long way in 50 years. Some new artificial limbs can restore wearers’ sense of touch or be controlled by wearers’ thoughts.
DARPA
 Electric limbs
Electric limbs