Notebook
-
 Life
LifeHow electric eels put more zip in their zap
With feisty prey, an electric eel curls its tail to intensify shocks and exhaust prey.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthParched parts of Earth expanding
More drylands, largely impacting developing nations, are forecasted for near future.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFurry, spiky mammal scampered among dinosaurs
Early Cretaceous fur ball with spikes discovered in Spain.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow to drink like a bat
Some bats stick out their tongues and throbs carry nectar to their mouths.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsEarly cyanobacteria fossils dug up in 1965
In 1965, early photosynthetic plant fossils were discovered. The date of earliest oxygen-producing life forms has since been pushed much earlier.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineElephants’ cancer-protection secret may be in the genes
An extra dose of cancer-fighting genes may be the secret to elephants’ long life spans.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsWhat really changes when a male vole settles down
Bachelor prairie voles can’t tell one female from another, but saying “I do” means more than just settling down.
By Susan Milius -
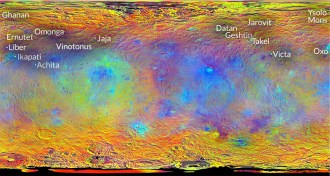 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceCeres mountains and craters named for food
A host of agricultural spirits are immortalized on several craters and mountains on the dwarf planet Ceres.
-
 Tech
TechEarly satellite TV predictions highlighted instant communication potential
Satellite communication started as science fiction but soon became reality.
-

-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMysterious circles appear, grow on comet
The Rosetta spacecraft caught five circular depressions quickly spreading across a region of comet 67P.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew dinosaur identified in Alaska
New species of duck-billed dinosaur discovered in the Alaskan permafrost.
By Meghan Rosen