Notebook
-
 Animals
AnimalsAn echidna’s to-do list: Sleep. Eat. Dig up Australia.
Short-beaked echidna’s to-do list looks good for a continent losing other digging mammals.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, fluoridation was promoted as a bone protector
In 1966, scientists hoped fluoride might protect adult bone health. While the results broke down over time, the benefits for teeth remain clear.
-
 Tech
TechDouble-charging material makes a run in the sun extra powerful
Textile stores energy from the sun and a person’s movements to power devices.
-
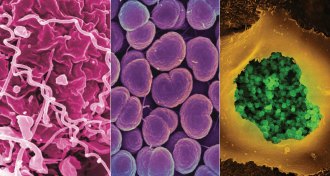 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCDC sounds alarm on STDs
The combined reported cases of three common sexually transmitted diseases reached a historic peak in 2015, a new CDC report says.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDragon dinosaur met a muddy end
‘Mud dragon’ fossil discovered in China suggests that dinosaurs’ last days were an active time of evolution.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years later, vaccines have eliminated some diseases
Vaccines have come a long way in 50 years.
-
 Earth
EarthMount St. Helens is a cold-hearted volcano
Geophysics reveals that deep beneath Mount St. Helens, there’s no source of hot magma, just a wedge of cold serpentinite rock. Where is the missing heat?
By Beth Geiger -
 Earth
EarthThe southern San Andreas has a smaller, neighboring fault to its west
The newly-discovered Salton Trough Fault runs parallel to the southern San Andreas Fault in California, potentially affecting the region’s earthquake risk.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRiding roller coasters might help dislodge kidney stones
Researchers took a 3-D printed kidney containing tiny stones and urine for a spin on a roller coaster and found their patients’ stories of kidney stones passing on the ride to have merit.
By Laura Beil -
 Earth
EarthThere’s a new way to stop an earthquake: put a volcano in its path
An earthquake rupturing along a fault in Japan was blockaded by the magma chamber below the Mount Aso volcano, researchers propose.
-
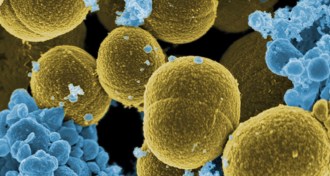 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStaph infections still a concern
Scientists have been searching for a vaccine against a deadly microbe for 50 years.
-
 Tech
TechHow to read a book without opening it
New technique allows scientists to read the pages of an ancient text without opening the book.