News
-
 Space
SpaceForget moon walking. Scientists want to give moon running a try
Researchers took over an amusement park attraction to test out an idea for how astronauts might exercise on the moon.
By Meghan Rosen -
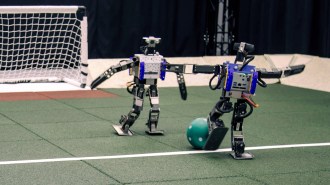 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceReinforcement learning AI might bring humanoid robots to the real world
Reinforcement learning techniques could be the keys to integrating robots — who use machine learning to output more than words — into the real world.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsTwo real-world tests of quantum memories bring a quantum internet closer to reality
Scientists successfully entangled quantum memories linked by telecommunications fibers across two different urban environments.
-
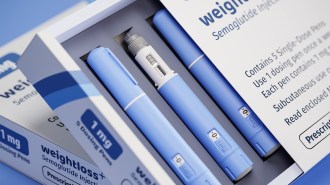 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYoung people’s use of diabetes and weight loss drugs is up 600 percent
Young people’s use of diabetes and weight loss drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy is surging, especially among females ages 18 to 25.
By Meghan Rosen -
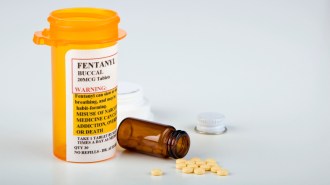 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTwo distinct neural pathways may make opioids like fentanyl so addictive
A study in mice looked at how feelings of reward and withdrawal that opioids trigger play out in two separate circuits in the brain.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHere’s how ice may get so slippery
Ice’s weirdly slick exterior might originate from the boundaries between two different types of ice that form on the surface of frozen water.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman body lice could harbor the plague and spread it through biting
Rats and fleas previously got all the blame, but humans’ own parasites could be involved.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsThe neutrino’s quantum fuzziness is beginning to come into focus
An experiment studying the neutrino’s “wave packet” sets a limit on the uncertainty of the subatomic particle’s position.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyOne of the world’s earliest farming villages housed surprisingly few people
Hundreds, not thousands, occupied the Turkish site of Çatalhöyük nearly 9,000 years ago, undermining arguments for a Neolithic social revolution.
By Bruce Bower -
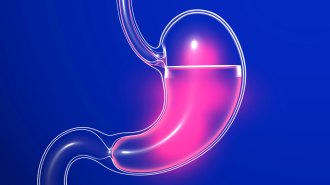 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBurning the stomach lining reduces the ‘hunger hormone’ and cuts weight
An experimental weight loss procedure blasts the stomach lining with heat to curb hunger and cut pounds.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsSumatran orangutans start crafting their engineering skills as infants
By 6 months old, young orangutans are experimenting with construction materials, and by 6 years old, they are building platforms 20 meters in the air.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGenetic analyses of the bird flu virus unveil its evolution and potential
The H5N1 outbreak in cattle is giving flashbacks to the COVID pandemic. But this time is different.