News
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA spot in the base of the brain has a love of language
Brain scans show a spot in the cerebellum attuned specifically to words, expanding on studies that point to the region's importance for language.
-
 Cosmology
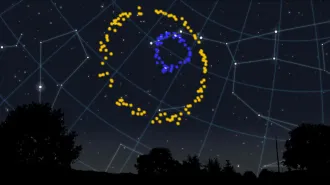
CosmologyA massive cosmic ring may challenge a key assumption about the universe
At 3.3 billion light-years across, the ring may challenge the “cosmological principle” that the universe looks uniform at sufficiently large scales.
- Anthropology
This hand stencil in Indonesia is now the oldest known rock art
The work suggests early Homo sapiens developed enduring artistic practices as they moved through the islands of Southeast Asia.
By Tom Metcalfe - Tech
This detached hand robot has a thing for skittering on its fingertips
The robot can bend, grasp and carry in ways humans can’t, which could help it navigate spaces too confined for human arms.
By Skyler Ware - Animals
This tool-using cow defies expectations for bovine braininess
Veronika the cow uses a brush as a tool to scratch herself, revealing rare problem-solving skills and expanding what we know of tool use in animals.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis fish may play a hole in its head like a drum
The rockhead poacher is a little fish with a big pit in its head. The divot may be like a drum, making sound that rises above a chaotic, nearshore din.
By Jake Buehler -
 Earth
EarthA long-lost tectonic fragment may be shaking Northern California
Seismic tremors reveal a shallow fragment of an ancient tectonic plate beneath Northern California, helping explain damaging earthquakes near the surface.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineColor blindness hides a key warning sign of bladder cancer
A large U.S. health records study suggests that difficulty seeing blood in urine may put color-blind patients at higher risk.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Animals
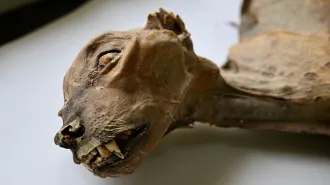
AnimalsHow cheetah mummies could help bring the species back to Arabia
Arabian cheetah mummies' DNA reveals that the long-lost population could be closely replaced by a cheetah population in northwestern Africa.
By Jake Buehler -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis dino’s fossil claw suggests it snatched eggs, not insects
A 67-million-year-old claw fossil reveals a new dinosaur species that may have used its hand spikes to snatch and pierce eggs.
-
 Plants
PlantsPlants packed close enough to touch are more resilient to stress
Signals transmitted via leaves can warn neighboring plants of stressful events, making the group collectively more resilient than plants in isolation.
-
 Climate
ClimateEarth’s last 3 years were its hottest on record
An analysis of global climate data shows sustained warming even as El Niño faded.