News
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMitochondria can sneak DNA into the nuclei of brain cells
An analysis of tissue samples from nearly 1,200 older adults found that the more insertions individuals had, the younger they died.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHow to spot tiny black holes that might pass through the solar system
Flybys of primordial black holes may occur once a decade. Tweaks to the orbits of planets and GPS satellites could give away their presence.
-
 Plants
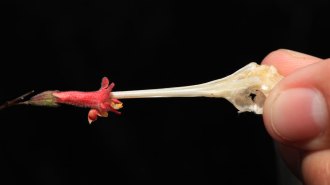
PlantsProjectile pollen helps this flower edge out reproductive competition
With explosive bursts of pollen, male Hypenea macrantha flowers knock some competitors’ deposits off hummingbird beaks before the birds reach females.
By Nala Rogers -
 Neuroscience
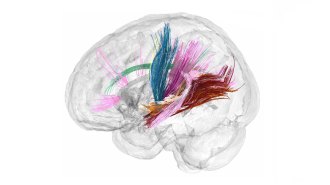
NeurosciencePregnancy overhauls the brain. Here’s what that looks like
Neuroscientist Liz Chrastil’s brain scans before, during and after pregnancy are providing the first view of a mom-to-be’s structural brain changes.
-
 Space
SpaceHow a dying star is similar to a lava lamp
In a first, astronomers captured how convective forces power the quick bubbling movement of gas cells on the surface of a distant, massive star.
-
 Climate
ClimateCan solar farms and crop farms coexist?
Researchers working in the field of agrivoltaics are studying how to combine solar farming with grazing, crop production or ecological restoration.
By Luke Groskin -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCan taking ashwagandha supplements improve health?
Ashwagandha is all over TikTok. Some studies report benefits, but more research is needed.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceScientists find a long-sought electric field in Earth’s atmosphere
The Earth’s ambipolar electric field is weak but strong enough to control the shape and evolution of the upper atmosphere.
-
 Life
LifeMega El Niños kicked off the world’s worst mass extinction
Long-lasting, widespread heat and weather extremes may have caused the Great Dying extinction event 252 million years ago.
By Jake Buehler -
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceTalking to a chatbot may weaken someone’s belief in conspiracy theories
AI might help lift conspiracy theorists out of the rabbit hole, but some researchers say proceed with caution.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Environment
EnvironmentHow much is climate change to blame for extreme weather?
Scientists can estimate how much more likely or severe some past natural disasters were due to human-caused climate change. Here's how.
By Maria Temming and Luke Groskin -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient DNA unveils a previously unknown line of Neandertals
DNA from a partial skeleton found in France indicates that European Neandertals consisted of at least two genetically distinct populations.
By Bruce Bower