News
-
 Tech
TechTech companies want small nuclear reactors. Here’s how they’d work
To fuel AI’s insatiable energy appetite, tech companies are going big on small nuclear reactors.
-
 Space
SpaceJWST spots the first known ‘steam world’
Astronomers have found a world shrouded in an atmosphere of water vapor, orbiting a star 100 light-years away.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOnce-weekly insulin might mean fewer shots for some with diabetes
Recent clinical trials of weekly insulin highlight how this formulation may be useful in managing diabetes, but the drug has limitations.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDoula care may lead to fewer C-sections or preterm births
A new study comparing the health outcomes of Medicaid patients with and without a doula suggests the extra support during pregnancy may be beneficial.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScience has finally cracked male riflebirds’ flirty secrets
New video upsets the old notion that these birds of paradise use wing clapping to make percussive sounds while courting.
By Susan Milius -
 Agriculture
AgricultureMegafire smoke may dampen California’s nut harvests
The summer after wildfire smoke blocked sunlight for long stretches, harvests at some almond tree orchards in California’s Central Valley dropped.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentAn idea to save Mexico’s oyamel forests could help monarch butterflies too
Climate change is putting monarch butterflies’ overwintering forests in Mexico at risk. Could planting new forests solve that problem?
-
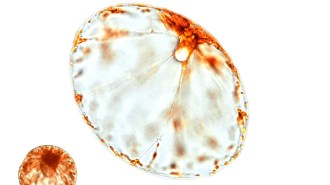 Oceans
OceansHow tiny phytoplankton trek long distances upward in the ocean
Taking in seawater while filtering out dense salts lets unicellular phytoplankton migrate tens of meters vertically toward sunnier seas.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThe cataclysmic origins of most of Earth’s meteorites have been found
Just a few smashups in the asteroid belt may account for 70 percent of Earth’s meteorites, limiting what’s known about our solar system’s history.
-
 Plants
PlantsCarnivorous plants eat faster with a fungal friend
Insects stuck in sundew plants’ sticky secretions suffocate and die before being subjected to a medley of digestive enzymes.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s Europa mission is a homecoming for one planetary astronomer
Over her long career, Bonnie Buratti has seen the search for life in the solar system go from a joke to a flagship mission.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAt-home experiments shed light on cats’ liquid behavior
Cats can flow like liquids through tall crevices, but they solidify a bit as they approach short crannies, new research shows.