News
-
 Plants
PlantsMosses frozen in time come back to life
Buried under a glacier for hundreds of years, plants regrow in the lab.
By Erin Wayman -
 Animals
AnimalsHow roaches developed disgust at first bite
A change in taste cells makes glucose-baited traps repellent.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeTests show that deadly flu could spread among people
Experiment shows that new influenza virus transmits through air between ferrets, a common experimental stand-in for humans.
-
 Life
LifeA molecular window on itch
Researchers discover chemical puppet master behind the need to scratch.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceGone perhaps, but Kepler won’t soon be forgotten
Astronomers look forward to building on the planet-hunting telescope's discoveries.
By Andrew Grant -
 Psychology
PsychologyLess is more for smart perception
Neural efficiency reigns in brains of high-IQ individuals as they view their surroundings, a new study indicates.
By Bruce Bower -
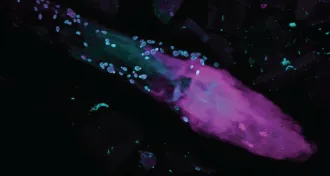 Life
LifeFoot fungi a thriving, diverse community
A skin census finds that toes and heels have the most fungal types.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeExperimental vaccine protects against many flu viruses
Ferrets that receive shot can fight off variety of influenza strains.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyDog sniffs out grammar
After years of word training, a canine intuitively figures out how simple sentences work.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeViruses and mucus team up to ward off bacteria
Phages may play an unforeseen role in immune protection, researchers find.
-
 Life
LifeInvasive frogs may spread deadly amphibian fungus
African clawed frogs imported for 20th century pregnancy tests apparently communicate B. dendrobatidis to native species.
By Susan Milius -
 Space
SpaceKepler mission may be over
The planet-hunting telescope has been crippled by the failure of two out of four pointing devices.
By Andrew Grant