News
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyChimps in captivity may soon join endangered species list
Proposal would extend protections to both wild and captive primate populations.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Tech
TechFaster memory could accelerate computing
Experimental microchip improves reliability and speed of writing and reading data.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsNow-extinct wolf may be ancestor of modern-day dogs
No strong signs of canine ancestry among living grey wolves.
-
 Tech
TechCamera captures voices without a microphone
Throat movements get decoded to reveal sounds of speech.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceResearch prods brain wiring underlying compulsive behavior
Complementary studies, focusing on repetitive grooming in mice, offer potential for new treatment strategies in humans.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTalk therapy helps Congolese victims of sexual violence recover
Groups sessions using a cognitive processing approach work better than individual support counseling, a study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsLight breaks up to cloak gaps in time
Method could hide messages without sender’s knowledge.
By Andrew Grant -
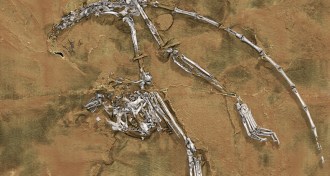 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossil sheds light on early primates
Partial skeleton near root of monkey, ape and human line.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsDead, live guppies vie for paternity
Females can use sperm months after mates go belly up.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFlu spreads via airborne droplets
Hand washing goes only so far in retarding flu transmission.
-
 Humans
HumansDietary changes accompanied human evolution
Hominids moved toward eating grasses and away from tree leaves, according to chemical analyses of fossil tooth enamel.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyItalians taught French wine-making
Archaeology suggests Etruscans brought the grape to Gaul.